Numerous scientific sources have repeatedly mentioned the benefits of breastfeeding for the baby. Despite this, many women choose formula feeding. This phenomenon is due not so much to the reluctance of the mother to give her baby breast milk, but to the various problems that the mother faces during lactation. The most common causes are chest pain and fever. Why do such phenomena occur? Do they indicate illness and can they harm the child? Consider these issues in the article.
How to respond to chest pain and fever?
Some women are ignored pain, since they are not intense, and the temperature of a nursing mother may not be high at all. Despite this, chest pain and fever are alarming symptoms that indicate the need to take measures to eliminate their causes.
Before taking action or inaction, every nursing mother should be examined by doctors who can pinpoint the cause of the pain.
Breast pain in nursing: causes of
As a rule, chest pain and fever in mothers after childbirth during lactation can be signs of the following processes and physiological characteristics:
- Change in the physiological state of the body
If pain occurs even before the start of direct feeding, this may indicate that the body is preparing for feeding the baby. The woman's body begins to produce oxytocin, which stimulates milk production and is responsible for filling the breast with milk. Chest pain can go unnoticed (slight tingling and slight discomfort) during the first few weeks of lactation, after which the mother's body stops producing oxytocin, and the woman gradually gets used to the process.
- Anatomical features
Very small, large, or flat nipples can also be painful during lactation. Note that with the correct position during feeding, the pain will disappear.
- Nipple problems
An increased local temperature in a nursing mother and pain may occur due to the characteristics of the nipples. So, many women at first may complain about the pain of lactation - undeveloped nipples gradually begin to harden, cracks and mastitis may appear. In this case, getting rid of painful sensations is very simple: it is necessary to determine the most comfortable position of the child, in which there will be no additional pressure on the chest and severe pain.
- Large amounts of milk
 Fever and chest pain can occur due to the production of large amounts of milk. As a rule, women eventually get used to these sensations (within 3 months) or begin to express excess milk already in the first weeks of breastfeeding.
Fever and chest pain can occur due to the production of large amounts of milk. As a rule, women eventually get used to these sensations (within 3 months) or begin to express excess milk already in the first weeks of breastfeeding.
- Narrowing of the breast ducts
This phenomenon is accompanied by the appearance of seals in the chest area and, sometimes, a febrile condition. This condition occurs as a result of infrequent feeding, excess milk and subsequent blockage of the excretory ducts. If left untreated, the problem can develop into mastitis. IN preventive measuresah, it is recommended to feed or pump every 2-3 hours.
- Thrush and other sexually transmitted diseases
It is known that diseases can be transmitted from mother to child during lactation. The closest contact between the baby and the mother is in the breast area, and therefore pain and temperature in the breast of a nursing mother may indicate the presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
- Stagnation and lactostasis
Even before the birth of a child, the body prepares for feeding - the producing cells of the mammary glands provoke their enlargement and development, which can be quick and painful at first. Breastfeeding mothers who have large breasts and ignore these phenomena can get lactostasis - an overflow of the mammary glands. As a result of these phenomena, there is often a fever and soreness in the chest.
- Breast diseases
Consider what treatments can be used to relieve chest pain and elevated temperature mothers with breastfeeding.
Treatment and prevention
 Chest pain and fever can be eliminated by observing preventive measures and direct treatment with medicines or folk remedies. Consider what actions you can take when a woman has severe chest pain after childbirth and heat:
Chest pain and fever can be eliminated by observing preventive measures and direct treatment with medicines or folk remedies. Consider what actions you can take when a woman has severe chest pain after childbirth and heat:
- In the case of mastitis or mastopathy, it is necessary to use only those drugs that the doctor prescribes. Due to improper treatment, the situation may worsen - the formation of infiltrative or purulent mastitis or chronic mastopathy. During this period, the temperature can be eliminated with the help of antipyretic drugs, and the pain - with the help of topical drugs.
- If chest pain is caused by cracked nipples, topical preparations (wound-healing creams and ointments) such as Purelan-100, Bepanten, etc. can be used.
- In the case of sexually transmitted diseases, the possibility of treatment with folk remedies and preventive measures is excluded. It is necessary to take medications that are indicated in the presence of accurate data on the disease.
- With the help of preventive measures, you can get rid of milk stagnation, lactostasis and a large amount of milk. Ice or cold compresses can be applied to the breast (for 15-20 minutes), which will improve milk flow, express regularly (depending on the volume of milk in the breast), avoid hypothermia and chest injuries. Of great importance is the correct position of the child during feeding, which is determined by mothers individually.
As a conclusion, we note: receiving funds traditional medicine, as well as the use of medications, is possible only after visiting a doctor and determining the exact cause of chest pain and temperature. Only after consultation can you choose measures to eliminate symptoms or treatment within the framework of the health of the woman and the child.
The reason deep pain in the chest (pain under the chest) are more often:
- dry or exudative pleurisy - inflammation of the pleura (connective tissue sheets that cover the lungs and ensure their mobility);
- hydrothorax - accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity;
- empyema of the pleura - accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity;
- pneumothorax - accumulation of air in the pleural cavity;
- pleuropneumonia - inflammation of the lungs, passing to the pleura;
- acute tracheitis or inflammation of the trachea - the cause of pain in the throat and chest;
- foci of pneumonia and tuberculosis located close to the pleura, abscesses;
- dissecting aortic aneurysm;
- aortitis - inflammation of the aorta;
- thromboembolism - blockage of the branches of the pulmonary artery by a thrombus or embolus.
Symptoms specific to your condition:
Probable diseases:
Cholelithiasis
Symptoms: sharp, constricting pain in chest, in the right side below the chest, extending into the neck and collarbone
Sharp, constricting pain in the chest, in the right side below the chest, radiating to the neck and collarbone, characteristic of diseases of the gallbladder, in particular for gallstone disease and biliary colic... A painful attack begins 3-4 hours after ingestion of fatty or spicy foods, more often in the late evening or at night. In search of a comfortable position, the patient rushes about in bed or wanders around the house all the time. Pressing pain in the chest increases and becomes burning, then weakens, becoming dull. Often an attack is accompanied by nausea, vomiting with an admixture of bile, bloating and diarrhea. It ends as unexpectedly as it began when the stone blocking the duct "falls" into the intestine. Simultaneously with the disappearance of chest pain, a large amount of light urine is excreted.
Diagnosis for severe right chest painand suspected cholelithiasis: analysis of the clinical picture, ultrasound of the liver and gallbladder, cholecystography, X-ray examination of the stomach and intestines.
First aid for chest pain, what to do with biliary colic: rest, cold on the right hypochondrium. It is urgently necessary to call the ambulance team and accompany the patient to surgical hospital department. It is forbidden to take painkillers before the arrival of the doctor, as this can hide the true picture of the disease.
Acute pneumonia
Symptoms: chest pain when breathing; high body temperature; chills; rapid and shallow breathing
Chest pain on breathing, high fever body, chills, rapid and shallow breathing typical for acute pneumonia... Croupous pneumonia is especially pronounced, in contrast to small-focal pneumonia, which can be manifested only by weakness, night sweats and a slight increase in temperature. With croupous pneumonia, there is reddening of the cheeks, blueing of the fingertips and mucous membranes, herpetic eruptions on the lips are common, severe pain in the chest, the patient has difficulty breathing. At first, the cough is dry in nature, then thick, viscous, jelly-like sputum, often brown or mixed with pus, begins to stand out.
x-ray examination is of decisive importance.
in the presence of respiratory failure - calling the ambulance team and delivering the patient to the pulmonary department of the hospital.
Acute tracheitis
Symptoms: moist cough; high body temperature; sharp pain in the middle of the chest, behind the sternum, aggravated by coughing; dry cough
Cough and sharp pain in the middle of the chest, behind the breastbone, aggravated by coughing, increased body temperature characteristic of acute tracheitis... Acute tracheitis often occurs with ARVI, including influenza, and is accompanied by all manifestations of a respiratory infection. The disease begins with an increase in body temperature, weakness, and increased fatigue. A little later, a runny nose, a feeling of soreness, perspiration or pain in the throat and chest appears. The cough, at first dry, harsh and painful, later gives way to wet, with discharge of mucopurulent sputum.
Diagnostics for severe cough, sore throat and chest caused by acute tracheitis based on the analysis of the clinical picture of the disease and the results of clinical research (examination, tapping and listening of the chest). With a protracted course of tracheitis, an X-ray examination of the lungs is shown.
First aid for chest pain and acute tracheitis: plentiful warm alkaline drink, for example, mineral water, milk, decoctions of expectorant fees, distracting procedures (hot foot baths, mustard plasters), alkaline inhalations (soda-oil). It is recommended to call the district therapist on house.
Lung or pleural cancer
Symptoms: persistent chest pain, stabbing, encircling, aggravated by coughing
Dry pleurisy
Symptoms: pain under the ribs, worse with a deep breath; dry cough
Dry cough, chest pain when breathing, pain under the ribs, worse with a deep breath, typical for dry pleurisy... Dry pleurisy often develops with tuberculosis, pneumonia, lung abscesses, pulmonary infarction, chest injuries, tumors passing to the pleura and other diseases. With pleurisy, there is a stabbing pain in the chest, which intensifies with deep breathing and tilting the body to the healthy side, and subsides in the lying position on the painful side. It is because of severe pain in the chest that patients lie mainly on their backs or on their sore side. The body temperature may be somewhat elevated, weakness, night sweats are noted. When examining the chest, you can notice some lag in the movements of the sick half from the healthy one.
Examination, palpation and listening of the chest, X-ray examination. maintaining the position on the sore side, taking painkillers. It is recommended to apply for medical care to a therapist or pulmonologist.
Exudative pleurisy
Symptoms: pain under the ribs, worse with a deep breath; heat; dyspnea; dry cough
Severe dry cough, chest painunder the ribs, sometimes shortness of breath characteristic of exudative pleurisy. Exudative pleurisy is an inflammation of the pleura, accompanied by the effusion of fluid into the pleural cavity and compression of part of the lung. The disease can occur with pulmonary tuberculosis, chest injuries, lung tumors. At first, while the effusion is in chest cavity a little, breathing problems do not arise, later, when a large amount of fluid accumulates, shortness of breath appears, chest pain, it is difficult to breathe. Body temperature with exudative pleurisy is increased, there is weakness, fatigue, night sweats. Examination of the chest often reveals swelling of the intercostal spaces on the affected side and a lag in breathing of the affected part of the chest.
Examination, probing, tapping and listening to the chest, X-ray examination.
If there are signs of respiratory failure, call the ambulance team and transport the patient to pulmonary department hospitals, with pain in the chest and no breathing problems - call the local doctor at home.
Various pains in any area of \u200b\u200bthe chest are often a serious symptom that requires an in-depth examination. Then, to quickly find out their cause, a modern range of various diagnostic methods is used. This complex is quite extensive, since pain in the areas of the sternum can indicate not only dangerous diseases, but also malfunctioning of many internal organs.
Some pain sensations are not dangerous at all, in fact, they are typical functional disorders. These include nervous tension or prolonged stressful conditions. However, most pains are urgently needed.
Causes of severe pain in the left and right chest area
Dangerous cardiovascular pathology often provokes the appearance of pain in the left half of the sternum. The list includes ischemic heart disease, dangerous, pericarditis, severe dissecting aortic aneurysm, aortic stenosis, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and pulmonary embolism.
With a significant lesion of the aortic arch, patients are concerned about pain on the right side in the chest. Their intensity varies, from dull aching with dangerous cardiomyopathy to incredibly burning acute pain with serious.
Often, pains provoke all kinds of diseases of the human gastrointestinal tract. Such as: gastric ulcer, reflux esophagitis, cholecystitis, esophageal spasm, hepatic colic and pancreatitis.
Pain from different sides occurs with pathologies of the pulmonary system. Dangerous pneumonia and pneumothorax, pulmonary emphysema, exudative and dry pleurisy, as well as tuberculosis and lung cancer, in addition to chest pains, are accompanied by such additional symptoms as shortness of breath and cough. Many patients often note an increase in chest pain when coughing.
Mental disorders such as psychogenic cardialgia, panic disorders, neurocirculatory dystonia, depression, perventilation and somatic neurosis indicate the nature of chest pain. Given the certain neurological status of patients, in some cases the nature and rather precise localization of these pains is possible. Often the pain is felt on the right side of the sternum, then on the left.
Diseases of the mammary glands can be bilateral in nature of pain. All kinds of diseases, tumors, mastopathy and mastitis, as well as malignant lesions of the glands, will give unpleasant sensations to a certain area. Severe pain is also provoked by a serious pathology of the spinal column. These experts include scoliosis,.
In some cases, quite severe pain in the chest appears due to various mechanical damage to internal organs. All kinds of bruises and, of course, rib fractures are always accompanied by unpleasant chest pains. When inhaling, pain is observed if the pulmonary pleura is damaged.
It should be noted that the correct diagnosis for various pains in the chest has a specific clear algorithm. A correct examination always begins with a study of the patient's specific complaints and an accurate determination of the nature of his pain. Depending on the nature of the sensations, electrocardiography is prescribed to quickly exclude the formidable ischemic disease hearts.
ECG and ultrasound data of the heart show the normal functioning of an important organ. Further examination includes changes in the nature of pain with different breathing, movements and depending on other factors. An increase in pain during inhalation indicates existing violations of the integrity of the lungs, or the penetration of air into an important pleural cavity. This condition causes pneumothorax.
With intercostal neuralgia, the pain itself changes during breathing and increases significantly with movement and even. After a complete study of all the patient's complaints and the history of the immediate disease, the doctor conducts the necessary instrumental and laboratory examination to make sure that the preliminary diagnosis is correct.
Burning sensation in the chest
A relatively strong burning sensation in the chest is a rather unpleasant sensation that constantly distracts from all normal daily activities. It interferes with the enjoyment of life, since severe malaise arises. Various diseases of the lungs and heart, the digestive system and mental disorders can be the main causes of burning in the chest.
Heartburn causes certain pain throughout the esophagus line. This burning sensation can last from a few minutes to several hours, while it is accompanied by sour belching. With frequent heartburn, it is recommended to undergo an examination first by a therapist, and then by a gastroenterologist. A severe burning sensation can also be the cause of a serious inflammatory disease of the esophagus, in other words. a symptom of reflux esophigitis. In this case, the pain is localized in the lower left side of the chest and is always permanent.
Often, a burning sensation in the chest indicates problems in the functioning of the heart. With angina pectoris, an insufficient amount of blood, nutrients and oxygen is supplied to the heart. Various cholesterol formations can cause this unpleasant condition. It often manifests itself with sufficiently active physical activity.
A burning sensation in the chest in various lung diseases is caused by inflammatory diseases, which are always accompanied by a significant increase in temperature and cough. Pain can be mixed to the left or right, depending on the specific lung affected. during bilateral pneumonia, a burning sensation can be observed on both sides. Also, flu and sore throat provoke the appearance of unpleasant sensations, which always come in combination with a sore throat and high body temperature.
Along with numerous diseases of the internal organs, a dangerous burning sensation in the chest is a symptom of one of the mental disorders, which is accompanied by apathy, loss of appetite and irritability. In this case, a visit to a psychologist is recommended.
Found a mistake in the text? Select it and a few more words, press Ctrl + Enter
Sharp chest pain

A sharp pain in the chest indicates acute illness one of the important internal organs. In such cases, you should definitely seek emergency qualified medical help. Such discomfort in the form of seizures should be examined more carefully on the basis of the patient's complaints, history, examination and ECG. Often, the diagnosis is made at the prehospital stage.
The main causes of such pain are serious diseases of the heart and blood vessels, respiratory and digestive organs, as well as ailments of the musculoskeletal system. Acute myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, pericarditis and myocardial dystrophy should be included in this list. In addition, it is necessary to note dissecting aortic aneurysm, pulmonary thromboembolism, as well as pneumonia, pleurisy, and spontaneous pneumothorax. There are frequent cases of esophagitis, ulcers and, chest radiculitis, trauma, shingles and neuroses.
Pressing chest pain
Unpleasant oppressive pain on the left side behind the sternum is the main symptom of angina pectoris. It is given to the left shoulder blade, arm or shoulder. The pain is intense enough that it instantly makes the patient freeze in place with his hand tightly pressed to the heart area. It should be mentioned that additional symptoms of an attack are pallor and cold extremities, increased heart rate and increased arterial pressure. Often, such attacks can occur after very active physical activity, when the heart's need for oxygen consumption increases significantly.
At the slightest suspicion of dangerous angina pectoris, it is recommended to immediately contact a cardiologist or at least a therapist. You will be scheduled for a routine examination that includes blood and urine tests, and an EKG. Basic treatment combined with diet and a healthy lifestyle allows the patient to quickly regain their well-being.
Dull chest pain
Dull pain can be the result of various ailments. But it is usually a symptom of pericarditis, which is a severe inflammation of the serous outer lining of the heart. This disease often indicates complications after infections. Dull, monotonous pain behind the sternum is of a moderate nature, from time to time becoming strong, reminiscent. Such unpleasant sensations are always localized on the left side of the chest.
Occasionally, such pains are combined with chills and fever, as well as general malaise and a significant change in general analysis blood. Only a cardiologist, after the necessary examinations, can diagnose and prescribe the correct treatment.
Fever and cough with chest pain
It has been proven if the characteristic pain in the chest of a person is accompanied by a cough and a significant increase in body temperature. then we can talk about serious inflammatory processes in the lungs. A sign of complication is the involvement in the process of pleural inflammation. Often, pain and cough occur with tracheobronchitis, while coughing up difficult sputum is observed. Inflammation of the lungs is characterized by severe pain with coughing, sudden fever and chills.
From the very first days, severe shortness of breath often appears, the heartbeat increases and the heart rhythm is disturbed. Dry pleurisy, like pneumonia, in most cases, is treated with the appointment of certain antibiotic therapy. Pleural puncture may be indicated if necessary.
During the breastfeeding period, a nursing mother may develop breast problems. Especially often young mothers who have had their first child suffer from this, since before this event there was no experience of latching a baby to the breast. When the mammary glands cause a woman discomfort, pain, and a rise in temperature occurs, this indicates that the disease begins: lactostasis or mastitis. How do they differ, and how to deal with these diseases?
There are many reasons that can lead to lactostasis or mastitis. It is important to understand in time what you are doing wrong in order to fix it, or to check if you are at risk, so as not to bring the disease to a severe form.
The chest hurts and the temperature rises suddenly due to:
- chronic stress, fatigue, lack of sleep;
- increased fat content of milk;
- long pumping;
- uncomfortable feeding posture;
- sleeping on your stomach or on one side;
- changes in sucking technique when the baby starts using the pacifier;
- anatomical structure of the breast;
- lack of a feeding regime (milk remains in the breast);
- wearing tight and uncomfortable underwear;
- hypothermia;
- improper attachment of the newborn to the mammary gland;
- lack of hygienic breast care;
- childbirth problems;
- viral infections, lowered immunity, lack of hemoglobin in the blood;
- cracked nipples.
All of these problems can lead to diseases that are severe. If you start everything, then there is a chance that a woman will be in a hospital with an infection, then the baby will be without breast milk.
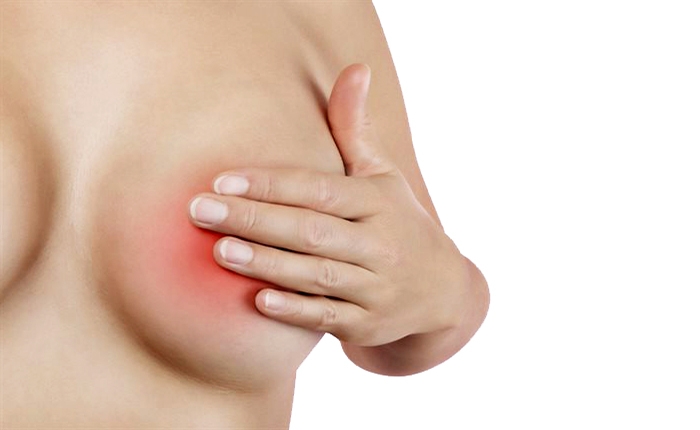
Lactostasis
Chest pain and fever speak primarily of lactostasis. This is called stagnation of milk in the breast with blockage of the milk ducts. This attack manifests itself in the first months of breastfeeding, when the production of breast milk has not yet been established, it arrives in the amount that the newborn does not need.
Main reasons:
- improper seizure of the nipple by the baby when feeding;
- incorrect body position during sleep and when feeding.
To prevent the onset of lactostasis, while still in the hospital, contact your medical staff for information on how to breastfeed properly. If this facility has not provided you with the assistance you require, you can always ask a feeding specialist.
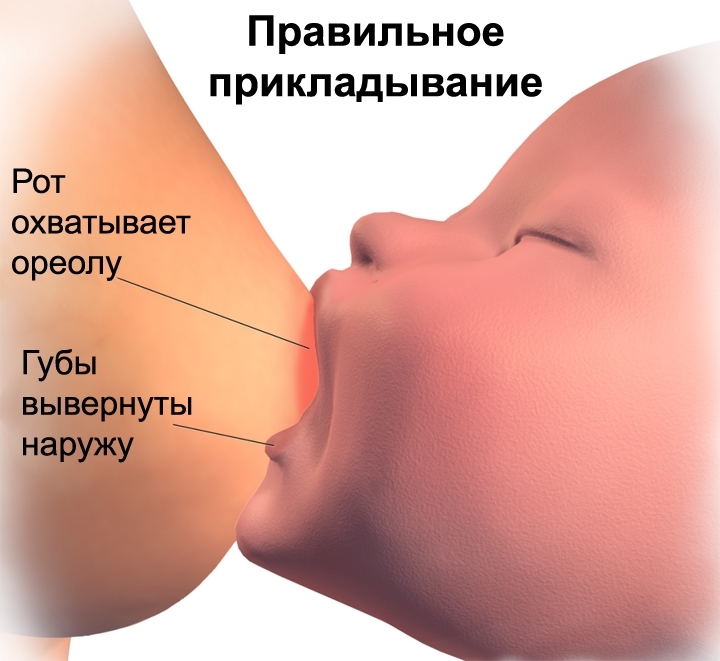
First, the correct feeding position is considered to be when the baby grasps the nipple and areola entirely, the mouth is wide open, and the lower lip is turned down. At the same time, a nursing mother should not feel pain. Secondly, wear a comfortable bra that will not pinch your breasts. Do not skimp on new underwear, what you wore before pregnancy will not come in handy in the near future, because your breasts are now increased by a size or more. Third, try to maintain a feeding schedule to improve milk production.
When the chest hurts and the temperature of 37 ° has been holding for several days, and constant expression and frequent latching of the baby to the breast do not alleviate the situation, but, on the contrary, adds more discomfort, contact your doctor at the antenatal clinic. Experts will be able to give the necessary recommendations: what ointment or gel you can use, how to massage your breasts, and if necessary, prescribe medications that will not interrupt breastfeeding.

Mastitis
If a nursing breast hurts and the temperature rises to 39 °, then this indicates the transition of lactostasis to a more severe form - mastitis.
In the course of the disease, it happens:
- serous;
- infiltrative;
- purulent.
Serous - this is the first stage of mastitis, which is easier to deal with, you need to urgently seek help from a specialist who will prescribe the necessary treatment.
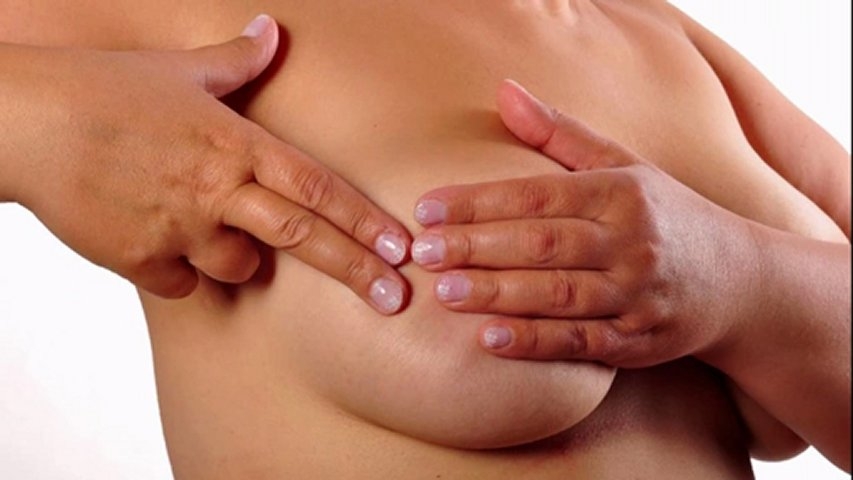

When the chest hurts and the temperature with HB are not the only symptoms, and to this are added thickening in the chest, redness of the skin, difficulty in expressing, then mastitis has passed into the next - infiltrative form of the disease. At this stage, it is very important to urgently see a doctor in order to correct the situation.
It is important not to allow the development of a purulent form, which will keep the heat at 39-40 °, there will be unbearable pain when feeding and even a light touch, cyanotic skin areas will appear where milk stagnation has occurred, pus will be released from the nipples with milk. It is required to immediately stop feeding, call an ambulance.
In the hospital, a nursing woman will be cured with antibiotics; you will have to refuse feeding for the period of treatment.
Diagnostics
It is very difficult to independently distinguish mastitis from lactostasis, because the symptoms are similar (chest pain and temperature up to 38 °). However, with mastitis, red patches of skin appear on the chest, the chest is thickened, swollen, even a slight touch or friction causes severe pain.
You should not diagnose yourself without visiting a doctor and resort to folk remedies. At best, you will waste time; at worst, you will make the situation worse. To make a diagnosis, the mammologist will refer you to a blood and breast milk test, an ultrasound of the mammary glands.
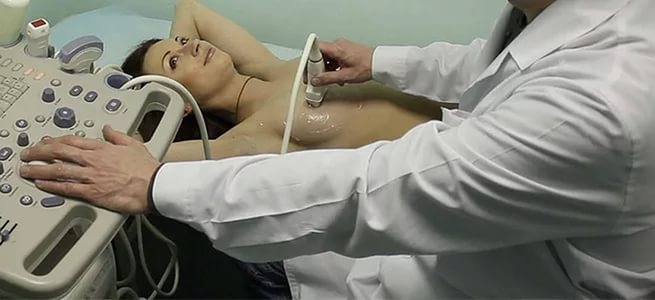
Treatment
Do not treat symptomatically: by drinking an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic, you will not cure mastitis, but only put your health and children's health at risk. The bacteria will begin to divide in an enhanced mode, after a while the pain will flare up with renewed vigor.
When the chest hurts and the temperature rises during breastfeeding, you should immediately visit the doctor in the antenatal clinic. The doctor will prescribe the necessary treatment, give recommendations on how to behave when feeding, explain what drugs can affect the child. Now there are many medicines that can heal the breast without weaning the baby from it.
The main principle is to express milk from a diseased breast as often as possible, even if the breast hurts and the nursing woman has fever. Purchase a high-quality breast pump for this procedure, express after each feeding (every two hours) the remains until you feel the feeling of heaviness in the mammary gland disappear. Then, apply ice wrapped in a bag and cloth.

You can also massage your breasts in a warm shower, moving in a circular motion towards your nipples.
If a specialist has prescribed antibiotics, then breastfeeding should be suspended until complete recovery. You can not feed either a diseased mammary gland or a healthy one! When a woman with mastitis has a fever above 38 °, you can take an ibuprofen tablet, cracks on the nipples are treated with Bepanten. With such a disease, sometimes a cabbage leaf is applied to the diseased breast, it will relieve inflammation, but only in the initial stages of mastitis. If everything is started, the doctor may prescribe surgical treatment.
Prevention
In order to prevent stagnation of milk in the milky lobules, you need to follow some rules.
- Wear comfortable underwear that is not tight or tight.
- Take care of your breasts, starting from pregnancy, temper it by washing it with cool (but not cold!) Water, wiping it off with a coarse towel. Before feeding, carry out hygiene procedures with the breast, wash your hands, and do the same after feeding the baby.
- Don't expect cracks to heal on their own. Now there is a large selection of ointments and gels that will cure this ailment in a short time.
- Latch the baby correctly to the breast, in the first month of his life, let us suckle at the first request, in order to then build a regime and establish the flow of milk.
- Try not to be in a draft, during breastfeeding, women's breasts are especially sensitive, it is easy to get cold.

If you follow these simple rules, then you will not learn from your own experience what lactostasis and mastitis are!
Video
How to get rid of lactostasis and avoid mastitis, you will learn from our video.
According to statistics, about 16% of lactating mothers, especially from among primiparas, suffer from advanced stagnation of milk in the ducts (lactostasis) and, as a result, mastitis.
Therefore, if a woman's chest hurts and the temperature rises sharply to 38 - 39 ° C, urgent action is needed.
Despite the fact that modern medicine successfully treats mastitis, it is advisable to eliminate the possible root causes of this unpleasant and dangerous disease. In the treatment of mastitis, accurate diagnosis is important, since its symptoms are similar to lactostasis, but the treatment of pathologies is fundamentally different.
Etiology
If during breastfeeding the chest hurts and the temperature rises suddenly, the cause of this phenomenon may be neglected lactostasis or mastitis.
Reasons for lactostasis:
- the structure of the breast, provoking the formation of a milk plug;
- squeezing the breast with a hand while feeding, sleeping on one side, feeding in an uncomfortable position, wearing tight clothes, etc.;
- prolonged pumping;
- stress causing a spasm of the milk ducts;
- chronic fatigue;
- high fat content of milk;
- using a pacifier that changes the baby's sucking technique;
- hard work with monotonous hand movements.
Lactostasis sometimes develops into mastitis.
Factors provoking mastitis:
- irregular feeding or feeding at intervals of more than 2 hours;
- persistent milk residues in the breast;
- cracks in the nipples through which the infection penetrates;
- anemia, reduced immunity;
- violation of hygiene standards and poor nursing breast care;
- tight, tight bra;
- hypothermia;
- improper baby feeding, poor, incomplete pumping;
- viral infections;
- history of breast pathology;
- complications during delivery, suppuration.
What is the difference between lactostasis and mastitis
If a nursing woman has chest pain and fever, this condition can be caused by both lactostasis and mastitis.
Milk stagnation, especially in primiparous, can be difficult to distinguish from the onset of mastitis.
Their symptoms are largely the same, but there are differences.
A sign of mastitis is a sharp rise in temperature up to 39 ° C against the background of swelling of the nipple, chills, chest pain.
With lactostasis, the duct is clogged, the thickening and redness of the skin is local, the temperature is low. If this condition lasts a week or more, mastitis may develop.
Types and symptoms of mastitis
 With mastitis, the chest hurts, the temperature is 38 ° C and above, the symptoms progress quickly. If not treated in any way, one stage can turn into another in literally 3 days.
With mastitis, the chest hurts, the temperature is 38 ° C and above, the symptoms progress quickly. If not treated in any way, one stage can turn into another in literally 3 days.
Varieties of mastitis
- Serous.
- Infiltrative.
- Purulent.
The serous variety is not characterized by a high fever, the breast enlarges and becomes painful.
Infiltrative mastitis is manifested by seals, on palpation of which unbearable pain is felt. The temperature is very high, the skin on the chest turns red, becomes hot and elastic.
With a purulent form, the chest swells greatly, increases, reddens at the site of the inflammation, it hurts unbearably and with light touch. Migraines and weakness occur. Pus is noticeable in the milk, the lymph nodes in the armpits are enlarged. The temperature can reach 40 ° C, and then drop, fluctuating.
With unilateral suppuration, you can feed the baby, but only with a healthy breast, since the bacteria can easily be passed on to the newborn.
Diagnostics
When the chest hurts and the temperature with HV for some signs (red painful spots on the chest, high temperature), self-diagnosis of mastitis can be carried out. But on early stage it is difficult to distinguish it from stagnant milk.
If you suspect mastitis, you cannot start treatment on your own without consulting a gynecologist and laboratory data. Mastitis should be treated as soon as possible, and without identifying a specific pathogen, it is impossible to choose the right drug or folk remedy... Also folk methods not designed for quick effect.
Diagnostics includes examination by a mammologist, ultrasound, blood test, breast milk.
If the diagnosis of mastitis is confirmed, antibiotics will be prescribed on the basis of the studies carried out, including some modern means that can be used for feeding.
Why is self-medication dangerous?
 Self-medication is dangerous by incomplete getting rid of the infection, when the symptoms are temporarily stopped, while bacteria continue to divide and inflammatory process flashes with renewed vigor. The application of cabbage leaves and other remedies that may be helpful in treating lactostasis are inappropriate for the treatment of mastitis. Home remedies are slow-acting and ineffective for severe infections. As a result, the disease will progress.
Self-medication is dangerous by incomplete getting rid of the infection, when the symptoms are temporarily stopped, while bacteria continue to divide and inflammatory process flashes with renewed vigor. The application of cabbage leaves and other remedies that may be helpful in treating lactostasis are inappropriate for the treatment of mastitis. Home remedies are slow-acting and ineffective for severe infections. As a result, the disease will progress.
Therefore, when the chest hurts and the temperature rises even slightly during feeding, the algorithm of actions should begin with a trip to the doctor.
Therapy
The basic principle of mastitis therapy is regular and complete pumping. For this purpose, it is convenient to use a high-quality expensive breast pump or seek help from your husband.
Since the newborn can be breastfed at an early stage, breastfeeding should be started on the diseased breast, even if there is pain. Before the process, put 4 drops of "Oxytocin" under the tongue to enhance the outflow of milk and eliminate spasms. You can also take a warm (but not hot) shower and gently massage your breasts in light circular motions towards your nipples. Then you need to express the remaining milk by hand and using a breast pump until the feeling of heaviness disappears. After the procedure, apply ice wrapped in cellophane and cloth to the chest for 15 minutes.
The actions must be repeated every 2 hours, including at night. In this case, it is important to correctly apply the baby to the breast - so that the lower lip is in the place of hardening.
Taking most of the antibiotics needed to treat advanced mastitis is a contraindication to feeding.
With normal milk stasis, drug therapy may not be required.
Particularly severe cases of purulent mastitis are treated only promptly, so it is important not to start the pathology.
Medicines
 To bring down the temperature from 38.5 ° C, antipyretics based on paracetamol or ibuprofen are shown.
To bring down the temperature from 38.5 ° C, antipyretics based on paracetamol or ibuprofen are shown.
In the presence of cracks in the nipples, local therapy with Purelan-100, Bepanten and other means is used.
Early diagnosis and timely treatment of mastitis avoids taking antibiotics.
Prevention
Prevention of mastitis and lactostasis includes:
- local hardening of the nipples, for example, daily washing the breast with cool water, rubbing with a coarse towel, starting from the gestation period;
- washing hands and breasts before feeding;
- correct attachment to the breast of the newborn;
- timely elimination of cracks in the nipples - a source of penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the mammary glands;
- feeding in the first month at the first request of the child;
- use of comfortable bras without hard parts cutting into the body.
Breastfeeding should avoid drafts and blows to the chest. If there is a history of mastitis, it is recommended that you express milk after each feed (but this is a controversial point). Therefore, preventing milk duct blockages lies in correct, frequent and regular feeding. In the presence of stagnant processes in the chest, you should immediately consult a doctor so that lactostasis does not develop into mastitis.
