LARYNGITIS.
it inflammation of the larynx mucosa. May be acute and chronic.
Laryngitis Acute.
Rarely isolated. More often this is one of the manifestations of acute respiratory disease, influenza, scarlet fever, whooping cough, etc. Its development is facilitated by general and local hypothermia, overexertion of the voice, inhalation of dusty air, irritating vapors and gases, inaccuracies in nutrition, smoking, alcohol abuse.
Symptoms for.
Feeling of dryness, soreness, soreness, scratching in the throat; the cough is dry at first, and later accompanied by the discharge of sputum; the voice becomes hoarse, rough, or completely silent; sometimes pain when swallowing, headache, and mild fever. The duration of the disease usually does not exceed 7-10 days. Under unfavorable conditions, it can turn into a subacute or chronic form. With laryngoscopy, diffuse hyperemia and swelling of the laryngeal mucosa are noted. The vocal folds are thickened, hyperemic, on them lumps of viscous sputum, during phonation they do not completely close. With the flu, hemorrhages in the mucous membrane (the so-called hemorrhagic pharyngitis) are possible. If pathological changes are observed only on one side of the larynx and laryngitis has taken a protracted course, it is necessary to exclude tuberculous, syphilitic lesions, neoplasms.
Treatment.
Elimination of the causes of the disease. For complete rest of the larynx for 5-7 days, the patient is advised not to talk. It is forbidden to smoke, drink alcohol. It is also necessary to exclude hot seasonings, spices. Useful warm drink (milk, borjomi), gargling decoction of chamomile or sage, warm alkaline inhalation, inhalation of aerosols of antibiotics
, warmth on the neck (bandage or warming compress), hot foot baths (42-45 ° C for 20-30 minutes). Apply also physiotherapy methods: sollux on the front of the neck, ultraviolet irradiation,
electrophoresis of novocaine
on the larynx area, UHF andmicrowave therapy.
Laryngitis Chronic .
As a rule, it occurs under the influence of the same reasons as acute inflammation, but acting constantly and for a long time. As a result, tissue trophism is disrupted and a dystrophic process develops.
Depending on the nature of these disorders, there are Catarrhal, Hypertrophic and Atrophic
forms of chronic laryngitis.
Chronic catarrhal
laryngitis. accompanied by chronic inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa, often diffuse.
Symptoms
Hoarseness, rapid fatigue of the voice, soreness, sore throat, periodic cough with phlegm. All these signs are enhanced with exacerbation of laryngitis. With laryngoscopy, a diffusely thickened, moderately hyperemic mucous membrane is visible, the vocal folds are thickened, injected blood vessels are visible on them; sometimes paresis of the internal muscles of the larynx is simultaneously noted, which is manifested by incomplete closure of the glottis during phonation.
Treatment.
Gentle voice mode; exclusion of factors contributing to the disease; oil and alkaline inhalation, aerosol inhalation antibiotics; elimination of errors in power supply; prohibition of smoking and drinking. When coughing - codeine. Useful warm drink (milk, borzhom). Effective application physiotherapy procedures (UHF, microwave therapy, electrophoresis novocaine on the larynx area, sollux, ultraviolet irradiationthe front of the neck).
Chronic hypertrophic laryngitis
characterized by proliferation of the epithelium and submucosal layer. May be limited or diffuse.
Symptoms
Hoarseness, sometimes reaching aphonia, feeling of awkwardness, burning, sore throat, cough with exacerbation of laryngitis. With laryngoscopy - a uniform thickening of the laryngeal mucosa, more pronounced in the area of \u200b\u200bthe vocal folds. With a limited form, hyperplasia of individual sections of the laryngeal mucosa is determined, more often the vocal folds or vestibular folds, the subglottic space, the inter-head region. It should be differentiated from specific infectious granulomas (tuberculosis, syphilis, etc.) and tumors.
Treatment
the same as in chronic catarrhal laryngitis.
In addition, after anesthesia of the laryngeal mucosa, hyperplastic areas cauterize with 3-5% silver nitrate solution... Areas of pronounced hyperplasia removed endolaryngeally surgically.
Chronic atrophic laryngitis
manifested by thinning and atrophy of the laryngeal mucosa. As a rule, it is one of the components of the atrophic process in the mucous membrane of the upper respiratory tract.
Symptoms
Feeling of dryness, perspiration, sore throat, dry cough, hoarseness. With laryngoscopy, the mucous membrane looks thinned, dry, covered with thick mucus, dried in places in the crust. With increased coughing, blood-streaked crusts may come off.
Treatment
mostly symptomatic.
Apply alkaline and oil inhalations, lubrication of the larynx with Lugol's solution in glycerin... For better removal of crusts, you can prescribe inhalation of aerosols of proteolytic enzymes (chymopsin, chymotrypsin, etc.).
PHARYNGITIS.
Is it spicy or chronic inflammation pharyngeal mucosa.
Pharyngitis Acute.
Rarely isolated, more often combined with acute inflammation upper respiratory tract (influenza, catarrh of the respiratory tract, various infectious diseases). An isolated lesion of the pharyngeal mucosa can be observed with direct exposure to irritants, such as prolonged breathing through the mouth and talking in the cold, smoking, alcohol, hot and cold food, etc.
Symptoms for.
Feeling of rawness, sore throat, slight pain when swallowing (more pronounced when swallowing saliva, with the so-called empty throat, than when swallowing food). Body temperature can be subfebrile. The general condition, as a rule, suffers little. With pharyngoscopy, the mucous membrane of the pharynx, including the palatine tonsils, is hyperemic, in places on it mucopurulent deposits, sometimes on the back wall of the pharynx separate follicles appear in the form of red grains, the tongue is edematous. In children younger age (up to 2 years) the disease is more severe. It is more often combined with inflammation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa and acute catarrhal rhinitis. Nasal breathing is impaired. Acute pharyngitis should be differentiated from catarrhal angina.
Treatment
predominantly local - the same as with angina.
Pharyngitis Chronic
.
Distinguish atrophic, catarrhal and hypertrophic forms.
It develops from acute pharyngitis if irritants acting on the mucous membrane of the pharynx are not eliminated for a long time. Contribute to the occurrence of chronic pharyngitis, runny nose, tonsillitis, purulent inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, dental caries, metabolic disorders, diseases of the heart, lungs, kidneys, etc.
Chronic atrophic pharyngitis,
as a rule, it is combined with atrophy of the nasal mucosa (see. Atrophic rhinitis).
Symptoms
.
Feeling of dryness, perspiration, scratching in the throat, often dry cough, rapid fatigue of the voice. With pharyngoscopy, the mucous membrane back wall the pharynx looks dry, thinned, pale, shiny, as if covered with a thin layer of varnish; it is often covered in mucus, drying in the form of crusts.
Treatment
symptomatic:
Rinsing with alkaline solutions, oil and alkaline inhalations, lubrication of the mucous membrane with Lugol's solution in glycerin. Inside - vitamin A, 3% potassium iodide solution
Pharyngitis is chronic, catarrhal and hypertrophic.
Symptoms
.
Feeling of perspiration, rawness, foreign body in the throat, moderate pain when swallowing, congestion in the pharynx of a large amount of viscous mucous discharge, especially in hypertrophic pharyngitis, which causes a constant need to cough up and expectorate. Coughing is especially severe in the morning, sometimes accompanied by nausea and vomiting. Pharyngoscopy: thickening and diffuse typremia of the pharyngeal mucosa; viscous mucous or mucopurulent secretion on it; enlarged separate groups of follicles appear. The soft palate and uvula are swollen and thickened. With the hypertrophic form of pharyngitis, these symptoms are more pronounced. The accumulation and enlargement of the lymphoid tissue of the posterior pharyngeal wall, the so-called granules, is referred to as "granular pharyngitis", and the hypertrophy of lymphoid tissue on the lateral walls of the pharynx behind the posterior palatine arches in the form of bright red ridges is called "lateral pharyngitis". These terms designate hypertrophic forms of pharyngitis.
Treatment.
Rinsing with alkaline solutions, inhalation and spraying; lubrication of the mucous membrane of the pharynx with Lugol's solution with glycerin, 2-3% collargol solution orprotargol.
With Hypertrophic pharyngitis
- cauterization of granules with 5-10% solution of silver nitrate, trichloroacetic acid. With pronounced hypertrophic forms of pharyngitis, apply cryotherapy.
ANGINA. TONSILLITIS.
Acute Angina.
A nginbut acute (tonsillitis) is a common acute infectious-allergic disease, in which there is inflammation of the lymphadenoid tissue of the pharyngeal tonsils, more often the palatine tonsils
By etiology, acute tonsillitis are divided into 3 types:
- Primary tonsillitis (common)
- one of the most common diseases of the upper respiratory tract.
Etiology.
Common sore throats can be caused by: staphylococcus, streptococcus, pneumococcus, fungi of the genus Candida, anaerobes, adenoviruses, influenza viruses.
Transmission mechanism - airborne, contact-household and alimentary route from sick or bacterial carriers to healthy ones.
The provoking factors are hypothermia, decreased immunity, irritation.
Symptoms
Primary tonsillitis are acute inflammatory processes only the lymphadenoid ring of the pharynx.
With streptococcal sore throat, toxins are released into the bloodstream, intoxication of the whole body occurs, possibly damage to the nervous, cardiovascular, and immune systems. Frequent sore throats can lead to rheumatism, - Secondary (symptomatic) tonsillitis.
It manifests itself in acute infectious diseases (infectious mononucleosis, scarlet fever, tuberculosis, adenovirus, herpes, etc.), in systemic blood diseases (agranulocytosis, leukemia, etc.), the tonsils are also affected. - Specific sore throats - the etiological factor is a specific infection (for example, Simanovsky-Plaut-Vincent's angina, fungal tonsillitis).
Clinical symptoms of angina.
The disease begins acutely. They complain of chills, pain when swallowing, rawness, sore throat, fever.
Regional lymph nodes become enlarged and painful to the touch. The severity of clinical symptoms depends on the severity of angina.
According to clinical forms, acute tonsillitis are:
- catarrhal,
- follicular,
- lacunar,
- phlegmonous,
Catarrhal angina.
In this case, mainly superficial damage to the tonsils occurs. Body temperature up to 37.0. Moderate intoxication.
Objectively: hyperemia of the soft and hard palate, posterior pharyngeal wall, moderate enlargement of the tonsils.
The catarrhal form can turn into another form of angina (lacunar or follicular).
Lacunar and follicular tonsillitis
proceed with more pronounced symptoms.
The body temperature rises to 39-40 "C, the symptoms of intoxication are more pronounced (general weakness, headache, pain in muscles, joints, throughout the body). General analysis blood detects leukocytosis, an increase in ESR up to 40-50 mm / h. Traces of protein, erythrocytes, are sometimes found in urine.
Lacunar Angina.
There is a defeat of the tonsils in the area of \u200b\u200bthe lacunae with a purulent coating on the free surface of the palatine tonsils.
A yellowish-white fibrinous-purulent plaque does not go beyond the tonsils, it is easily removed without leaving a bleeding defect.
Follicular tonsillitis.
In this case, mainly the follicular apparatus of the tonsils is affected.
Objectively: the tonsils are hypertrophied, sharply edematous, suppurating follicles in the form of whitish-yellowish formations the size of a pinhead are visible (picture of a "starry sky"). Suppurative follicles open up, forming a purulent plaque that does not spread beyond the tonsils.
Angina phlegmonous or peritonsillar abscess.
This is an acute purulent inflammation of the periaminal tissue. More often it is a complication of one of the forms of angina described above. It rarely develops, most often against the background of chronic tonsillitis.
The process is often one-sided. Patients complain of a sharp sore throat when swallowing, headache, chills, weakness, fever up to 38-39 gr. There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, profuse salivation .. Regional lymph nodes are significantly enlarged and painful on palpation.
Objectively: with pharyngoscopy, a sharp hyperemia and swelling of the tissues of the soft palate on one side is noted. If the treatment is not carried out on time, then a limited abscess may form in the peritoneal tissue - a peritonsillar abscess. If it is not opened on its own, then a surgical opening of the abscess is performed while taking antibiotics. Inflammatory changes in the lymphadenoid pharyngeal ring do not always indicate angina.
Differential diagnosis should be carried out with diphtheria, measles, influenza, acute catarrh of the upper respiratory tract, including acute pharyngitis, infectious mononucleosis, from acute diseases blood.
Complications.
Peritonsillitis, paratonsillar abscess, purulent lymphadenitis of regional lymph nodes, sinusitis, otitis media, tonsillogenic mediastinitis, phlegmon of the neck, rheumatism, meningitis, nephritis.
Treatment of Angina.
Bed rest on the first day.
Food is soft, gentle, drinking plenty of fluids (milk with honey, tea with lemon) .
- Antibacterial drugs: broad-spectrum antibiotics or prescribe antibiotics based on bacterial sowing, anti-inflammatory drugs. In the case of the development of phlegmonous sore throat, opening the abscess is shown, taking antibacterial drugs.
- Rinsing:various antibacterial solutions are used for rinsing. As antiseptics, a 1% solution of iodinol is used for washing the throat, a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide, a 0.1% solution of potassium permanganate, a 2-4% solution of boric acid, a solution of bicarminth, 0.05-0 , 1% solution of rivanol, calendula tincture;
- Inhalation:use decoctions of the following herbs - chamomile, eucalyptus, marigold flowers, Siberian elderberry, etc.;
- Compresses:it is recommended to apply compresses, especially with enlarged regional lymph nodes.
A mixture of alcohol (100 ml) + menthol (2.5 g) + novocaine (1.5 g) + anestezin - menovazin (1.5 g) apply to the front of the neck, wrapping the neck with a warm cloth or scarfm.
Chronic tonsillitis.
it chronic inflammation of the tonsils; both adults and children are ill. The reason is repeated tonsillitis, less often other acute infectious diseases (scarlet fever, measles, diphtheria). The development of chronic tonsillitis is promoted by persistent violation of nasal breathing, decreased immunity, chronic sinusitis, rhinitis, sinusitis, dental caries, gum disease, etc.
In case of exacerbation, they are treated in the same way as acute angina. And, it is necessary to cure chronic diseases that contribute to the development and exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis.
LARINGOSPASM.
More common in early childhood, with rickets, spasmophilia, hydrocephalus or due to artificial feeding, etc., and is explained by an increase in the reflex excitability of the neuromuscular apparatus of the larynx. In adults, it can be the result of reflex irritation of the larynx by a foreign body, inhalation of irritating gases.
Symptoms for.
In children - periodic attacks of convulsive closure of the glottis with prolonged noisy inhalation, cyanosis, twitching of the limbs, constriction of the pupils, sometimes with respiratory arrest, rarely loss of consciousness. The attack usually lasts a few seconds and breathing is restored. In adults, an attack of laryngospasm is also short-lived and is accompanied by strong cough, facial flushing, and then cyanosis.
Treatment.
Elimination of the cause of the disease. During an attack irritate the mucous membrane (tickle in the nose, give a sniff of ammonia) and skin (face spraying cold water, prick, pinch). Intubation or tracheostomy is very rare.
In the interictal period, restorative treatment is carried out (walks in the fresh air, vitamin therapy, especially vitamin D
). Infants prone to laryngospasm and who are bottle-fed should be provided with donor milk whenever possible.
LARRY OTHER.
Occurs as one of the manifestations inflammatory or non-inflammatory lesion of the larynx and is usually localized in places of accumulation of loose pod of the mucous tissue of the larynx (subglottic space, vestibular folds, scary laryngeal folds, surface of the epiglottis from the side of the tongue).
May be limited or diffuse.
Causes: trauma (mechanical, thermal, chemical) of the mucous membrane of the pharynx or larynx, allergies, acute infectious diseases, diseases of the cardiovascular system and kidneys, collateral edema with pathological changes in the cervical lymph nodes, thyroid gland, with inflammatory processes in the pharynx (peritonsillar, parapharyngeal abscess, etc.); phlegmon of the neck with acute, especially phlegmonous laryngitis, with neoplasms of the larynx.
Symptoms and course depend on the localization and severity of the edema. They may consist only of a feeling of awkwardness, mild sore throat when swallowing, or be more serious up to a sharp difficulty in breathing. In this case, significant stenosis of the larynx lumen often occurs. With laryngoscopy, a limited or diffuse, tense, gelatinous, tumor-like formation of a pale pink color is visible. The contours of the anatomical details of the larynx in the area of \u200b\u200bedema disappear.
Treatment.
The patient is hospitalized, as even a slight edema can increase very quickly and lead to severe stenosis of the larynx. If possible, it is necessary to eliminate the causes of edema. The patient is given swallow ice cubes, place an ice pack around the neck, prescribe distraction therapy (mustard plasters, cans, hot foot baths), inhalation of oxygen, inhalation of aerosols of antibiotics, antibiotics in / m, sulfonamides, dehydration therapy (intravenous infusion of 20 ml 40% glucose solution), intravenous injection 10 ml 10% calcium chloride solution,1 ml 5% ascorbic acid solution... Also shown intranasal novocaine blockade, diuretics antihistaminesdrugs inside, i / m ( pipolfen, suprastin, etc.), inhalation of aerosols of corticosteroids... In severe cases, enter i / m 1 - 2 ml of hydrocortisone (25-50 mg) or intravenous 1-2 ml of an aqueous solution prednisone(slowly for 4-5 minutes). With the failure of drug therapy and an increase in laryngeal stenosis, tracheostomy (or prolonged intubation).
STENOSIS OF THE LARYNX.
This is significant reduction or complete closure of its lumen.
Distinguish acute and chronic
laryngeal stenosis.
Acute stenosis may occur suddenly, lightning fast, or develop gradually over several hours. Observed with true and false croup, acute laryngotracheobronchitis in children, laryngeal edema, phlegmonous laryngitis, chondroperichondritis, foreign body, trauma (mechanical, thermal, chemical), bilateral paralysis of the posterior cricoid muscle.
Chronic stenosis characterized by the slow development of narrowing of the lumen of the larynx and its resistance. However, during the period of chronically occurring narrowing of the larynx under adverse conditions (inflammation, trauma, hemorrhage, etc.), acute stenosis of the larynx can rapidly develop. Chronic stenosis occurs on the basis of cicatricial changes in the larynx after trauma, chondroperichondritis, scleroma, with diphtheria, syphilis, tumors.
Symptoms and course
depend on the stage of stenosis.
Stage I - compensation - accompanied by the loss of a pause between inhalation and exhalation, lengthening of inhalation, a reflex decrease in the number of breaths and a normal ratio of the number of respiratory movements and pulse. The voice becomes hoarse (with the exception of stenosis due to paralysis of the lower laryngeal nerves), a stenotic noise appears on inspiration, which is heard at a considerable distance.
Stage II - decompensation:all the signs of oxygen starvation clearly appear, shortness of breath increases, the skin and mucous membranes take on a bluish tint, when inhaling, there is a sharp retraction of the intercostal spaces, supra- and subclavian fossa, and the jugular fossa. The patient becomes restless, rushes about, becomes covered with cold sweat, breathing: becomes more frequent, respiratory noise intensifies. Stage III - asphyxia (suffocation) - characterized by a fall, cardiac activity, breathing is rare and shallow, the pallor of the skin increases, patients become lethargic, indifferent to the environment, pupils are dilated, persistent cessation of breathing, loss of consciousness, involuntary discharge of feces and urine. To assess the degree of stenosis, the size of the glottis lumen is most important. However, with a slow increase in stenosis, the patient sometimes copes satisfactorily with breathing with a narrow larynx lumen. When establishing the diagnosis, tracheal stenosis, respiratory distress due to diseases of the lungs and heart should be excluded.
Treatment.
With any disease of the larynx, if the danger of stenosis is not excluded, the patient should be urgently hospitalized in order to take all the necessary measures to prevent asphyxia in a timely manner.
At the stage of compensation it is still possible to restore breathing by therapeutic methods (mustard plasters on the chest, hot foot baths, inhalation of oxygen, medications morphine groups, dehydration therapy, cardiac drugs).
In the stage of decompensation and asphyxia must be done immediately tracheostomy (in recent years, extended intubation has been successfully used), with diphtheria stenosis - intubation. In case of respiratory arrest after opening the trachea, artificial lung ventilation is performed. In patients with chronic stenosis, treatment should be directed to the underlying disease (tumor, scleroma, etc.).
With cicatricial stenosis, bougienage and surgical methods of treatment are used - laryngo- and tracheostomy with excision of scar tissue.
PHARINGOMYCOSIS.
This is a lesion of the mucous membrane of the pharynx with a fungus leptotrix.
On the surface of the mucous membrane of the posterior pharyngeal wall, lateral ridges, in the lacunae of the tonsils, whitish dense formations appear in the form of thorns, tightly sitting on the base. They arise as a result of increased proliferation of the epithelium with keratinization! These spines are clearly visible on pharyngoscopy. Pharyngomycosis is facilitated by long-term irrational use of antibiotics, chronic tonsillitis, hypoavitaminosis. The course is chronic, not disturbing the patient; the disease is often discovered by chance on examination of the pharynx. Only sometimes does the patient indicate an unpleasant sensation of something foreign in the throat. In laboratory research, leptotrix fungi are found in dense thorns.
Treatment.
Lubrication of the mucous membrane and tonsils with Lugol's solution with glycerin. Gargling and washing lacunae with 0.1% aqueous solution of quinosol (2 times a week, a total of 8-10 times). With concomitant chronic tonsillitis, it is shown removal of tonsils.
SCLEROMA.
It is a chronic infectious disease that affects the lining of the respiratory tract.
The causative agent is the Frisch-Volkovich stick. Ways and methods of infection have not been established.
Symptoms for.
The disease is characterized by a slow course that progresses over many years. In the initial stages, dense infiltrates are formed in the form of flat or bumpy eminences, which, as a rule, do not ulcerate, are located mainly in places of physiological narrowing: on the eve of the nose, choans, nasopharynx, the laryngeal lining space, at the tracheal bifurcation, at the bronchial branches. In a later stage, the infiltrates are scarred, thereby causing a narrowing of the airway and respiratory distress. Usually, a scleroma captures several sections of the airway at the same time. Less often, the process is localized in one area.
Diagnosis
.
To recognize the scleroma process, the serological Wasserman, Borde - Zhangu tests, histological examination of biopsy material and the study of sputum on Frisch - Volkovich sticks are used. It is necessary to take into account the patient's residence in the area where scleroma occurs.
Treatment.
There is no specific treatment. A favorable result is obtained with treatment streptomycin and X-ray therapy... TO surgical methods treatments include bougienage, removal and electrocoagulation of infiltrates.
Normal 0 false false false RU X-NONE X-NONE
Sore throat treatment
At the onset of the disease, it is necessary to comply with bed rest (to reduce the possibility of developing complications - from the heart, kidneys, joints). Spicy, rough food is excluded from the diet. It is recommended to drink plenty of warm drink (milk with honey, tea with lemon), broth, liquid porridge, jelly (all from a separate dish).
Drug therapy involves the use of antibacterial drugs (selected on the basis of culture, or broad-spectrum antibiotics) and anti-inflammatory drugs. The treatment regimen can only be prescribed by an experienced doctor after examination. Self-medication can lead to undesirable outcomes. In the case of the development of phlegmonous tonsillitis, the first stage is shown to open the abscess.
Concomitant therapy:
- rinsing: various antibacterial solutions are used for rinsing. As antiseptics, a 1% solution of iodinol is used for washing the throat, a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide, a 0.1% solution of potassium permanganate, a 2-4% solution of boric acid, a solution of bicarminth, 0.05-0 , 1% solution of rivanol, calendula tincture;- inhalation: for inhalation, decoctions of the following herbs are used - chamomile, eucalyptus, marigold flowers, Siberian elderberry, maned carragon (camel's tail), common blueberry, etc.; - compresses: Local compresses are recommended, especially for enlarged regional lymph nodes. A mixture of alcohol (100 ml), menthol (2.5 g), novocaine (1.5 g), anesthesin - menovazin (1.5 g) apply to the front of the neck, wrapping the neck with a scarf or scarf
There are many signs of throat and larynx disease. Symptoms and causes of throat and larynx disease:
- dry mouth;
- sore throat;
- stuffy nose or ear;
- headache;
- painful sensations while swallowing;
- increased body temperature (depending on the type of disease);
- the appearance of white plaque on the tonsils;
- dry cough, as if tearing the throat;
- pain in the lymph nodes when pressed;
- redness of the throat;
- purulent plugs in the throat;
- swelling of the mucous membrane and other signs.
 Remember that only the correct and timely started treatment contributes to recovery. Do not forget that any treatment should be followed through and not abandoned at the first sign of improvement. The fact is that a disease that has not been completely cured often turns into a chronic form, which will be much more difficult to get rid of. By the way, many ailments that have become chronic have a negative effect on the internal organs of a person, so they should be avoided.
Remember that only the correct and timely started treatment contributes to recovery. Do not forget that any treatment should be followed through and not abandoned at the first sign of improvement. The fact is that a disease that has not been completely cured often turns into a chronic form, which will be much more difficult to get rid of. By the way, many ailments that have become chronic have a negative effect on the internal organs of a person, so they should be avoided.
The causes of throat or larynx disease are:
- the presence of tumors;
- injury to the throat or larynx;
- diseases of the thyroid gland;
- fungal infection, as well as other pathogens that affect the mucous membranes;
- external factors (smoking, alcohol abuse, carbonated drinks, etc.).
The most common acute diseases of the larynx and throat are:
- Pharyngitis.
- Angina.
- Adenoiditis.
- Laryngitis.
- Laryngeal edema.
The most common chronic diseases are:
- Laryngeal stenosis.
- Movement disorders.
Now is the time to consider each of the above ailments in more detail.
Pharyngitis
This disease of the throat and larynx is expressed in inflammation of their mucous membranes. It is rarely an independent disease. As a rule, pharyngitis occurs due to inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, which occurs in an acute form.
The main symptoms of pharyngitis are:
- feeling of tickling;
- painful sensations when swallowing;
- purulent plaque on the mucous membrane of the throat.
 If you do not start timely treatment of the disease, and also do not eliminate all the factors that have a very negative effect on the inflamed mucous membrane, the acute form of the disease will soon turn into a chronic one. By the way, it is she who often appears in people suffering from caries, tonsillitis, kidney disease, as well as chronic rhinitis.
If you do not start timely treatment of the disease, and also do not eliminate all the factors that have a very negative effect on the inflamed mucous membrane, the acute form of the disease will soon turn into a chronic one. By the way, it is she who often appears in people suffering from caries, tonsillitis, kidney disease, as well as chronic rhinitis.
During angina, as is correct, the lymphadenoid tissue of the tonsils becomes inflamed. This disease can be both infectious and allergic. Therefore, they are distinguished into the following three types of angina:
- primary;
- secondary;
- specific.
The most common is the primary angina caused by various fungi and viruses. This disease is contagious and is transmitted from person to person by household or airborne droplets. A person can be a carrier of this disease for a long time, but it is aggravated as a result of hypothermia or a decrease in immunity.
Secondary sore throat appears after a person has contracted some kind of viral infection, such as scarlet fever or measles.
Specific types of pathogens are the cause of specific angina. Antibiotics must be used to treat them.
Adenoiditis
This disease is caused by a virus that infects the pharyngeal tonsil. Its main symptoms are:
- difficulty breathing;
- severe headaches;
- purulent rhinitis;
- suffocating cough, which occurs mainly at night.
If you do not start timely treatment, soon this disease will develop into an even more serious one, for example, tonsillitis, otitis media or sinusitis.
Laryngitis
In the event of this disease, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the vocal cords is noted. Usually, laryngitis is not an independent disease, although there are exceptions. As a rule, it manifests itself against the background of SARS, influenza, whooping cough and other diseases.
- dry cough;
- sore throat;
- hoarseness of voice;
- pain while swallowing;
- thickening of the vocal cords.
Laryngeal edema
Never arises on its own. Most often, it is preceded by purulent tonsillitis, phlegmonous laryngitis and other diseases.
By the way, laryngeal edema is caused not only by inflammation, but also by an allergic reaction provoked, for example, by food, household chemicals or cosmetics. Moreover, it can be caused by any injury to the area.
Laryngeal stenosis
In the event of this disease, the larynx is partially or completely blocked. It occurs in both acute and chronic forms. The acute form is the result of a foreign body entering the larynx or injury. It can also occur due to phlegmonous laryngitis and a huge number of other reasons.
In chronic stenosis, the larynx narrows gradually. It arises as a consequence of many diseases, for example, syphilis, as well as in the presence of scars on this organ from old injuries and surgical interventions.
Movement disorders
They are expressed in stopping the work of the larynx, which can be complete or partial. This is facilitated by inflammation of the muscles or laryngeal nerves.
The following diseases can provoke movement disorders:
- traumatic brain injury;
- syphilis;
- intracranial hemorrhage;
- sclerosis, etc.
Treatment
Regardless of what kind of disease your throat or larynx is suffering from, you should start treating it immediately. Only in this case it is possible to eliminate the root cause of the disease and prevent it from becoming chronic.
Only a doctor has the right to determine the treatment regimen. At the same time, he takes into account the form of the disease, the reasons for its occurrence, the patient's condition, as well as many other related factors.
So, for example, pharyngitis is usually treated with drugs that have an exclusively local effect. These can be special sprays, lozenges, lozenges, or throat gargles.
If you have to treat laryngitis, then first of all it is necessary to completely eliminate the cause of its appearance. Inhalation and foot baths are also helpful.
But the treatment of angina is not complete without taking antibiotics. Remember that the doctor should prescribe them. The fact is that there are simply a huge number of such drugs, each of which acts in its own way and has its own side effects. The doctor, after examining the patient and making him the above diagnosis, must determine which of the antibiotics is best suited for the treatment of a particular type of angina.
If the throat disease is caused by any fungal infection, it will be possible to choose the correct treatment regimen only after receiving the results of laboratory tests.
Prevention
In order for diseases to overwhelm a person as rarely as possible, it is necessary to regularly carry out prevention. This is facilitated by long walks in the fresh air, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, moderate exercise and much more.
And after the onset of the first cold weather, the throat should be taken care of with special care. Try to rinse it with a solution of salt or soda at least twice a day, use a scarf and avoid hypothermia.
If you still have the first symptoms of a cold, you must:
- talk less to preserve your vocal cords;
- drink plenty of fluids;
- completely abandon the use of alcoholic beverages and tobacco;
- exclude foods that irritate the throat (seeds, chips, carbonated drinks, etc.).
By adhering to these simple rules, you can prevent the development of the disease. But if you still have a sore throat, then treatment should be started immediately.
Contents
Almost every one of us has once faced such a problem as a sore throat. As a rule, throat diseases occur in autumn or winter, but there are cases when such a symptom occurs in summer or spring. In most cases, the throat is severely sore due to the development of a bacterial or viral infection, or irritation of the mucous membrane. It is also very painful to swallow in the early stages of the development of colds.
So why does throat disease occur? Throat problems can occur for a variety of reasons, but we will discuss the most common ones. In most cases, various throat diseases arise for the following reasons:
- the development of a fungal infection;
- weakened immunity;
- avitaminosis;
- low humidity levels;
- unbalanced diet or prolonged fasting;
- dental diseases;
- side effects of various medications;
- allergic reactions;
- inhaling smoke, which irritates the airways and irritates the throat;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- the development of infection in the nasopharynx;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules;
- after oral sex;
- due to chemical irritants;
- after burns.
Painful sensations can have various forms, for example, aching, acute, pressing, dull,. Also, the pain can have a pulsating, subsiding or increasing character, and the place of its location can be different. To determine the cause of severe sore throat, you need to consult a doctor who, after a diagnosis, will be able to diagnose and prescribe treatment. In most cases, the diagnosis consists in passing the following tests:
- listening to the upper respiratory tract;
- a smear taken from the throat;
- monitoring the level of acid in the esophagus;
- chest x-ray;
- measuring pressure in the esophagus;
- x-ray of the neck.

Symptoms
Most often, throat diseases are accompanied by various symptoms, the main of which we will consider today. So how do the symptoms of throat disease exist?
- increased body temperature;
- runny nose;
- it hurts to yawn;
- burning;
- headache;
- mild fever;
- cough;
- something saliva;
- increased sensitivity along the entire neck;
- sneeze;
- increased salivation;
- general tiredness;
- hoarseness.
It is also worth drawing your attention to the fact that the reason why the throat is very sore and may be the development of a viral or bacterial infection. Naturally, only a doctor can determine the cause of a throat disease, but for some reason people constantly ignore this and treat the disease on their own. In the event that sore throat is caused by the development of a bacterial infection, the sore throat will be sudden and severe enough. The most common bacterial infection is streptococcal infection. If the throat hurts a lot due to a bacterial infection, then the following symptoms will be observed:
- an increase in body temperature up to forty degrees Celsius;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- it hurts terribly to yawn.
But still, the most common causes of various throat diseases are viral infections. In this case, the inflammation develops gradually, which means that the severity of the symptoms will also increase gradually. Viral diseases include diseases such as influenza, measles, chickenpox, mononucleosis, and the like. If throat diseases are caused by the development of a viral infection, then the following symptoms arise:
- an increase in temperature, but there are times when the body temperature remains normal;
- dry cough;
- fatigue quickly arises.

Treatment
What is the treatment for throat problems? Due to the increase in swelling of the mucous membranes of the throat, pain, which at any tension of the vocal cords can lead to an increase in sore throat. In this case, eating food and even swallowing liquid will be accompanied by pain. In most cases, the treatment of throat disease consists in taking antibiotics to treat a bacterial infection, but if the disease is complicated by various complications, then the treatment is slightly complicated depending on the severity. Note that treating a bacterial infection is different from treating a viral one. The difference is that only the treatment of a bacterial infection consists in taking antibiotics, and with a viral infection, taking antibiotics is unacceptable. Improper treatment of throat diseases can lead to complications such as:
- kidney disease;
- purulent sore throat;
- rheumatic heart disease.
Also, the treatment of throat diseases may be accompanied by the use of anesthetics, which contain ingredients that cause numbness in the throat and reduce pain, but do not be afraid that you will stop feeling your throat altogether. You can also use menthol sweets, which can also reduce sore throat and cool and soften the throat. But note that menthol candy cannot cure the disease itself.
In addition, the doctor may prescribe antiseptic and antibacterial sprays, which contain components that help stop the multiplication of the infection. Pay attention to the fact that when there is pain in the throat, it is quite difficult and even painful to swallow food, and sometimes saliva, so dehydration may occur. The likelihood of developing dehydration increases significantly if there is a fever. In this case, the patient needs to consume more fluid.
![]()
What can be done at home to reduce sore throat?
- gargle more often with warm saline, but in no case swallow it;
- take pain relievers;
- try to strain your vocal cords less;
- stop smoking, as this irritates the throat;
- eat cold foods such as ice cream to reduce the risk of dehydration.
- observe bed rest;
- monitor your breathing and breathe better through the nasopharynx;
- more often carry out wet cleaning in the room in which the patient is located;
- drink as little liquid as possible;
- use antibacterial lozenges and cough lozenges more often to.
What to do if a sore throat hurts, and treatment with medications prescribed by a doctor is of little help?
- Gargle with horseradish tincture. To prepare it, you need to mix a tablespoon of horseradish with a teaspoon of ground cloves and 240 grams of warm boiled water.
- Raspberry broth for gargling. Pour two teaspoons of raspberry leaves with a glass of boiling water and leave for ten minutes, and then strain through a strainer and cool.
- Gargle with a solution of lemon juice, for this you need to stir the lemon juice in 240 milligrams of warm boiled water.
- ... To prepare it, you need to pour two teaspoons of sage with a glass of boiling water and leave to infuse for ten minutes, and then strain through a strainer and cool.
- Gargle with linden tincture. To prepare it, you need to mix 40 g of dry linden with 60 g of medicinal chamomile, pour two glasses of boiling water and leave for an hour.
- Tincture based on cayenne pepper. In order to prepare it, you need to mix the juice of half a lemon with a tablespoon of salt and a quarter teaspoon of cayenne pepper, and then pour half a glass of warm boiled water.
It is necessary to gargle with the presented tinctures at least four times a day, otherwise the gargle will be ineffective.
Painful sensations in the throat quite rarely require an ambulance call, but there are exceptions:
- so severe pain in the throat that the patient cannot swallow saliva, and salivation is increased at the same time;
- severe swelling of the throat, which is accompanied by shortness of breath and slight wheezing when breathing.
A simple trip to the doctor can be limited only in such cases:
- high body temperature (about 38 degrees Celsius), which is not accompanied by any other signs of a cold;
- alternating high and low temperature body;
- pain when moving the jaw;
- purulent plugs are visible on the back of the throat;
- pain in the throat that lasts for 48 hours and is not accompanied by symptoms typical for colds;
- lymph nodes are greatly enlarged;
- hoarseness that lasts for two weeks.
Diseases of the throat and larynx are one of the most pressing problems of modern otolaryngology. Usually, people do not attach importance to such diseases, and such an attitude often leads to serious complications. Diseases of the throat and larynx are being diagnosed with increasing frequency, especially in children and young people. Inadequate therapy leads to the formation of foci of chronic infection, which adversely affects the state of the whole organism.
Diseases of the larynx: symptoms
- dryness and;
- high or low-grade fever;
- headache;
- pain when swallowing;
- pain in the lymph nodes, aggravated by palpation;
- unproductive cough;
- plaque in the throat;
- redness and swelling in the throat, enlarged follicles.
The most common diseases of the throat and larynx
Infection tonsillitismanifests itself as an inflammatory process in the tonsils, which are very important for the formation of the protective functions of the human body. The disease proceeds with recurrent sore throat, accompanied by intoxication and swollen lymph nodes. Tonsillitis can cause a variety of complications: arthritis, skin diseases, pyelonephritis, heart defects, thyrotoxicosis. The most effective treatment method is phonophoresis.
If the back of the throat becomes inflamed, the disease is called pharyngitis... The disease develops after exposure to cold or polluted air, as well as as a result of smoking, allergies or injuries. They provoke symptoms of the disease (pain when swallowing, dry cough, low temperature), pathologies of intestinal diseases or the consequences of ARVI. In the treatment, topical antiseptic drugs are used, as well as throat rinsing and inhalation.
When laryngitis the mucous membrane of the larynx becomes inflamed, the disease proceeds acutely or in chronic form.  Overexertion of the voice should be excluded, in some cases, even for a short while, abandon any conversations, exclude irritating components from food. Laryngitis is treated with inhalation, gargling and warming. As an addition to the main therapy, warm drinks are used (tea with raspberries, milk with the addition of borjomi, cocoa butter), throat wrapping and hot foot baths.
Overexertion of the voice should be excluded, in some cases, even for a short while, abandon any conversations, exclude irritating components from food. Laryngitis is treated with inhalation, gargling and warming. As an addition to the main therapy, warm drinks are used (tea with raspberries, milk with the addition of borjomi, cocoa butter), throat wrapping and hot foot baths.
With inflammation, the disease is called adenoiditis... Manifested by shortness of breath, snoring, frequent purulent rhinitis, recurrent otitis media, which can impair hearing. The cause of adenoiditis is viral infection... The most effective treatment is nasopharyngeal lavage in combination with laser therapy, sometimes surgery is performed.  Diseases of the throat and larynx must be treated in a timely manner, especially in chronic forms. To do this, you should visit a specialist. He will provide adequate therapy and rule out laryngeal tumors, which may be benign (more common) and malignant.
Diseases of the throat and larynx must be treated in a timely manner, especially in chronic forms. To do this, you should visit a specialist. He will provide adequate therapy and rule out laryngeal tumors, which may be benign (more common) and malignant.
Prevention
In order to prevent tumor-like formations, special attention should be paid to personal hygiene and measures to improve the conditions of life and work.
Throat diseases, photos and videos of which will be presented below, are very diverse. A person who is far from medicine believes that they are caused only by viruses or bacteria, but there are many more reasons. As for the symptoms, diseases of the larynx and pharynx have similar manifestations. However, there are some differences. When a sore throat is sore, a person should see a therapist, pediatrician, otolaryngologist, or general practitioner.
Pharyngitis in most cases occurs in combination with inflammatory processes in the upper respiratory tract, it can be SARS, influenza and a large number of other infectious diseases. The bacteria that cause this disease enter the mouth with dust, and cold air can also be the cause of pharyngitis. However, there is also an infectious form of the disease, it is caused by streptococci or staphylococci and various microorganisms.
With pharyngitis, there is a burning sensation, a lump in the throat, perspiration, pain, which intensifies when swallowing. The patient coughs, his temperature rises. In the acute form, purulent or mucous discharge is observed. Nasal breathing is difficult. The tongue in the throat is swollen, and the back of the throat may be covered with follicles. For pharyngitis in a chronic form, the characteristic symptoms are as follows: thinning and dryness of the mucous membrane of the back of the pharynx and mucus on it, which dries up and turns into a crust.
Pharyngitis is treated with inhalation, rinsing, vitamin therapy. It is advisable not to injure the throat with sour and spicy foods during treatment, hot and cold foods and drinks will also irritate the mucous membrane, so they should be at room temperature.
Inflammation of the larynx - laryngitis
This disease is most often associated with colds, infectious diseases, often the cause is hypothermia of the throat when inhaling cold air. Laryngitis can be provoked by smoking, inhalation of dusty air, overstrain of the larynx.
The disease begins with dryness and sore throat, pain may occur when swallowing. The temperature may rise slightly. The patient complains of an exhausting dry cough.
The main symptoms are redness of the throat and hoarseness, which can lead to a complete loss of sonority of the voice, the patient can only speak in a whisper. The cough becomes moist over time, a strong sputum separation begins. Often, patients say they are having trouble swallowing a lump in their throat. Sometimes the inflamed blood vessels may bleed. The disease is dangerous because the mucous membrane can swell very much and block the air supply, as a result of which a violation of brain activity or even a coma can occur.
There are a lot of forms of laryngitis and the treatment of each of them may differ slightly. Anti-inflammatory and expectorant drugs are mainly prescribed. In the acute form, local antibiotics are prescribed.
Some types of tonsillitis
Follicular angina always begins with high temperature... High temperature readings can last for a week. With follicular angina, the following symptoms occur:
- sore throat, which becomes worse when swallowing and can often be given to the ear;
- intoxication processes;
- swollen lymph nodes.
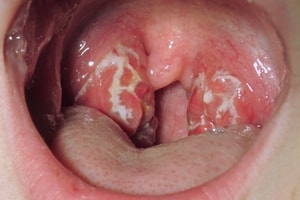 Purulent, or lacunar, sore throat is caused by streptococci, the pathological flora attacks both tonsils at once. The main causative agent is streptococcus. Symptoms of purulent sore throat:
Purulent, or lacunar, sore throat is caused by streptococci, the pathological flora attacks both tonsils at once. The main causative agent is streptococcus. Symptoms of purulent sore throat:
- lymph nodes are enlarged;
- strong pain;
- heat;
- lack of cough;
- feverish condition;
- weakness.
Adenoviral angina affects many organs. It is accompanied by diseases of the ear, throat, nose, inflammation of the larynx and pharynx, conjunctivitis develops. The disease begins with rhinitis, and then other symptoms that are characteristic of diseases of the throat and larynx join.
The Coxsackie virus provokes herpesvirus sore throat. The onset of the disease resembles the flu, while nasal congestion, intoxication manifestations are characteristic. Then on the palatine arches, on the softest palate, on the wall of the pharynx, small bubbles with liquid contents appear. After some time, the vesicles burst, and suppuration of the vesicles is a complication.
With fungal sore throat, severe pain also occurs in the throat. AT oral cavity a person constantly has a fungal infection, but with good immunity, it is not terrible for health. But as soon as immunity falls, the colonies of fungi increase dramatically and affect the mucous membrane of the mouth, as well as the pharynx and larynx.
Sore throats are mainly treated antibacterial drugs (with a fungal form, antifungal agents are prescribed). The patient is advised to gargle, dissolve medicinal lozenges, and take antipyretics at a temperature. Infusions and decoctions of medicinal herbs help well.
Measles, scarlet fever, rubella
Measles - viral disease throat, the diagnosis can only be made by a doctor. Measles begins with a high fever, and the skin becomes covered with small papules. Rashes can be seen on the oral mucosa and soft palate. At first they are scattered, and then they can merge into large red spots. The patient has a severe sore throat, general weakness and symptoms of intoxication.
Scarlet fever is caused by streptococcus. At the beginning of the disease, a typical catarrhal sore throat is observed: red throat, enlarged tonsils, gray films on the tonsils. If the process spreads into deep tissues, then the gangrenous-hemorrhagic form develops.
Another viral disease is rubella. It is also accompanied by rashes on the body and on the pharyngeal mucosa. There is no severe sore throat with rubella. But diphtheria is an infectious disease, the main symptom of which is a severe sore throat.
All these diseases can only be diagnosed by a doctor. He also prescribes treatment.
Other diseases:
- Stomatitis. Bad breath, strong saliva production, sore throat - these are the main symptoms of stomatitis. With aphthous stomatitis, round ulcers appear on the mucous membrane of the mouth, which can be the result of diathesis, intestinal diseases, they can also occur after flu or tonsillitis.
- Phlegmon of the mouth and a pharyngeal abscess can also cause sore throat. Phlegmon occurs with a complicated course of angina, with boils in the oral cavity, with injuries. However, the most common cause is an infectious process that spreads to the throat from carious teeth. A retropharyngeal abscess occurs only in children, the reason is the peculiarities of the development of lymph nodes.
- Babies may develop epiglottitis, an inflammation of the epiglottis. The disease is caused by Haemophilus influenzae. Symptoms are pain in grief, fever, swelling of the sinuses, voice changes. If you carefully examine the throat, you will notice redness and swelling in the epiglottis region.
- A sore throat is often associated with a lack of vitamins. With leukemia, with anemia, with glossitis, if there is osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebra, with cervical radiculitis, with neuroses (lump in the throat), with neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve, pain sensations of varying intensity occur.
Chronic diseases
When people talk about a chronic disease, they mean symptoms that bother a person for a long time. With this apparent reason infectious disease not visible.
Speaking about chronic throat diseases, you need to know that almost all acute forms of diseases can become chronic. For example, with frequent infectious tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis and other diseases, chronic inflammation in the tonsils can develop. This means that as soon as immunity decreases or favorable conditions arise, the infection will intensify and again lead to illness.
Chronic infections in the tonsils are a fungus, Haemophilus influenzae, streptococcus, staphylococcus, adenovirus and other pathological microorganisms. If you examine the tonsils, you can notice their enlargement, they will have plaque, while the color of the tonsils is normal. If the palatine arches are involved in a chronic process, then they can be thicker and fit tightly to the tonsils.
If chronic diseases are not treated, then the decompensated stage sets in. In this case, exacerbations will be very frequent, and other ailments (heart and kidney) may also join. In chronic pharyngitis, the patient complains of a constant lump in the throat, perspiration and minor pain.
Laryngitis in the chronic stage is characterized by dry mucous membranes and edematous vocal cords. In addition, a lump in the throat and dry crusts, which have grown tightly with the surface of the mucous membrane, may bother you. The patient coughs all the time, trying to get rid of the crusts, his voice is hoarse.
Complications of throat diseases and their prevention
Throat diseases often lead to the following complications:
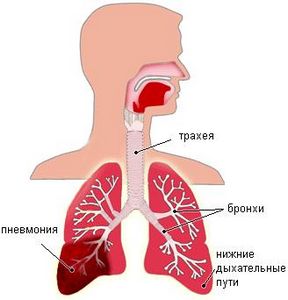
- pneumonia;
- chronic forms;
- abscesses;
- irreversible loss of voice.
Although the treatment of throat diseases, in principle, is not difficult, it is still better to prevent their occurrence. To do this, you need to strengthen the immune system, spend more time in the fresh air, get rid of bad habits (smoking), temper. As a preventive measure, you can regularly gargle with decoctions of herbs, which have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects.
Any diseases of the throat have a pathological effect on the nasopharynx area. If the throat is not treated in time, the infection can cause complications in the nasal cavity.
