Pain is one of the main alarm signals in the body, which haunts a person. People with a healthy psyche will certainly react to pain. Nerve endings are responsible for this sensation; pain can occur when they are irritated or inflamed. It is for this reason that we feel pain in the area of \u200b\u200ban abscess or bruise. Nerve endings should not be confused with nerve roots and trunks. Compression of them, on the other hand, leads to numbness and paralysis. Inflammation of the nerve endings can occur with various specific and nonspecific infections, when neuritis develops, for example, with herpes zoster or, as it is also called, shingles. But most often one has to deal with the fact that the initiator of the process is muscle spasm, and, as a result, the vessels are compressed in this area. Violation of blood supply leads to damage to the nerve endings.
What are the symptoms of nerve irritation?
How to recognize inflammation of nerve endings, symptoms of this disease? The main symptom is pain, while it is not possible to identify either the focus or visible changes indicating the disease. The pain may worsen in cold weather, during movement or at night, even with slight touch. Another characteristic feature is the so-called paresthesias: tingling and burning sensations in the affected area. Often in this area, spasmodic tense muscles, painful on palpation, can be found on examination.
Treatment of inflammation of the nerve endings
What can be the treatment for inflammation of nerve endings? To eliminate the symptoms of the disease, use medications: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, nise, movalis, etc.), glucocorticoid hormones (dexamethasone, prednisolone, etc.), B vitamins and other drugs. In addition, patients are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures (electrophoresis, phonophoresis, amplipulse, etc.). However, medications have many side effects and are unsafe for our body.
Can nerve inflammation be cured without medication? Our nervous system produces its own painkillers - endorphins and enkephalins, a person is subject to initiate or enhance their synthesis. In addition, special gymnastics allows you to relieve muscle spasm, improve blood supply in the inflammation focus and eliminate pain. There are also other methods and techniques for dealing with pain and inflammation. You can learn more about them at the special course of the M.S. Norbekova "The first health-improving course". will teach you to restore physical health, increase immunity, start regeneration processes, normalize the emotional background.
The main types of neuralgia
If a person has a cold nerve, the development of the inflammatory process will immediately let you know the pain syndrome and autonomic manifestations, i.e. increased sweating, hyperemia, myalgia, etc. The most common types of neuralgia are:
- trigeminal - inflammation trigeminal nerve;
- intercostal - compression of the roots of the spinal nerve roots;
- occipital - damage to the occipital nerve;
- radial and ulnar - compression of the nerve bundles located on the hands.
In the case of the development of any of the above types of neuropathy, the following general symptoms are observed:
- hyperthermia;
- marbling of the skin;
- irritability;
- fast fatiguability;
- pain at the site of localization of the affected nerve roots.
Occipital neuralgia
If a person has a chilled occipital nerve, they will experience severe headaches. Their appearance is due to the compression of the nerve roots by the surrounding tissues.
If untreated, the pain becomes permanent, and any head movements provoke nausea and dizziness.
The causes of occipital neuropathy include:
- muscle strain;
- endarteritis and gout;
- diabetes mellitus and osteochondrosis;
- trauma and hypothermia;
- infectious diseases (meningitis, encephalitis).
The main symptoms of a congested nerve will be:
- headaches;
- "Lumbago" in the lower part of the neck;
- increased pain when turning the head;
- sensitivity to bright light;
- hypo-hypersensitivity of the skin.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Infringement of the trigeminal nerve on the face in most cases is due to the following reasons:
- multiple sclerosis;
- hypothermia;
- violation of the bite;
- muscle strain;
- vascular aneurysms;
- viral and bacterial infections.
If a person has chilled the jaw nerve, the development of the inflammatory process will be signaled by:
- pain while chewing;
- numbness of the lower face;
- increased salivation;
- involuntary contraction of the jaw muscles;
- hypersensitivity of the skin.
Inflammation of the nerve on the arm
The hand is innervated by several nerve bundles, however, in the case of a negative impact of exogenous and endogenous factors, the radial, median and ulnar nerves are most often affected. The main causes of the onset of pathology include:
The following symptoms indicate a cold of the nerve on the arm:
- sharp and aching pains in the shoulder and arm;
- swelling of the affected limb;
- partial paresis;
- limited limb mobility;
- numbness of the fingers;
- decreased hand sensitivity;
- increased pain with muscle tension.
Intercostal neuralgia
A large number of nerve endings are located between the 12 pairs of ribs. In case of pinching of peripheral nerves in chest severe pain occurs under the scapula. If the clamping occurs on the left side, the symptoms of a neurological disease are often confused with pain in the heart. The causes of inflammation of the nerve endings can be:
- osteochondrosis and compressor fracture;
- hypothermia and hormonal imbalance;
- lung disease and anemia;
- multiple sclerosis and diabetes mellitus;
- scoliosis and kyphosis.
What symptoms signal inflammation if a person chills a nerve under the scapula?
- pain in the thoracic spine, radiating to the neck or lower back;
- violation of the sensitivity of the skin at the site of inflammation;
- burning and itching in the area of \u200b\u200bthe scapula;
- increased pain when sneezing, coughing and moving.
Methods for treating neurological diseases
Can a tense nerve be warmed up? Experts do not advise self-medication, as this can only aggravate the course of the disease.
Dry heat is used to treat neuropathy, but in the absence of abscesses in the affected tissues.
Warming up purulent foci of inflammation provokes the development of a bacterial infection, which can provoke severe complications up to paralysis.
To eliminate the disease, physiotherapeutic procedures, medicines and surgical intervention are used. Conservative treatment of a congested nerve is accompanied by the use of such drugs:
- antibiotics;
- analgesics;
- antidepressants;
- multivitamins;
- muscle relaxants;
- anti-inflammatory drugs.
List of the most effective drugs
How to heal a congested nerve? For a quick blockade of inflamed nerve bundles and their treatment, the following types of medications are used:
- "Sirdalud" is a muscle relaxant, the components of which act on the skeletal muscles, contributing to its relaxation;
- Finlepsin is an anticonvulsant drug that eliminates muscle spasms. It has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects;
- "Simbalta" is an antidepressant that is used in the treatment of peripheral neuropathy. Eliminates irritation and helps to normalize sleep;
- Sulindak is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that accelerates the regeneration of nerve fibers;
- "Metipred" is a glucocordicosteroid hormone that promotes the synthesis of lipocortin, which reduces inflammation.
conclusions
How is a congested nerve treated?
Neuropathy in 90% of cases is accompanied by severe pain in the affected areas of the body. Timely treatment helps prevent tissue abscess and complications.
To eliminate neuralgia, I use antidepressants, multivitamins, antibiotics and analgesics. They relieve the symptoms of neuropathy and promote decompression of the nerve roots.
How should trigeminal inflammation be treated? A neurologist will tell you about this. Neuralgia caused by inflammation of the trigeminal nerve affects the facial part of the skull, causing severe pain to a person in several parts of the body at once:
- in the neck;
- in the chin;
- in the jaws;
- in the nose;
- in the forehead and eyebrows.
Issues of etiology and therapy
The disease usually affects women over 50 years old. Although the disease tends to "get younger" every year, therefore, it manifests itself in young people. The following factors can cause an attack:
- 1. Hypothermia.
- 2. Exceeding the threshold of permissible physical activity.
- 3. Decreased immunity, as a result of which infection or harmful bacteria penetrates the human body.
Only a doctor can determine whether it is neuralgia or not, therefore, if pain occurs, an urgent need to go to a medical institution, and not self-medicate. Diagnosis involves compiling a medical history based on interviewing the patient about the symptoms that bother him and possible reason these processes, and then an MRI scan is assigned.
It is magnetic resonance imaging that is able to give an accurate picture of the state of the blood vessels and the human brain. Additional methods may be prescribed, but MRI is the most effective, accurately helping to differentiate inflammation of the trigeminal nerve from other diseases.
Therapy. The method of treatment will depend on what is causing the disease. Therapy can consist of several parts - medication and folk. It is not recommended to treat inflammation of the trigeminal nerve on your own, since the patient does not know what kind of pain needs to be eliminated. The doctor first of all prescribes drugs that can remove soreness and pain symptoms. These can be drugs that have anticonvulsant properties. They have the ability to suppress nerve cells and their activity, eliminating seizures.
These drugs include Baclofen or Tegretol, which are prescribed only after passing a detailed biochemical analysis. This is due to the fact that drugs have the ability to affect the liver, causing changes in them.
Among other medications, other medications are prescribed:
- 1. Vitamin complexes, which contain a lot of vitamin B. They can be prescribed both in the form of injections and in the form of tablets.
- 2. Novocaine or alcohol drugs that can block nerve branches. But taking such funds has a downside, since they reduce the effect over time. The more procedures are performed, the lower the blockade threshold.
- 3. Analgesics, among which Carbamazepine is most often prescribed. It is available in the form of tablets, it is the main one in the treatment of inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. Possesses a high level of analgesic effect. But it is forbidden to take it to pregnant and lactating mothers, since it has toxic substances in its composition. Among other contraindications, it is worth noting the negative effect on the respiratory, nervous, endocrine and other human systems, which does not prevent Carbamazepine from coping well with inflammation of the trigeminal nerve.
- 4. Antihistamines (for example, Pipolfen), which enhance the effect of analgesics.
- 5. Glycine, which is an adjunct to the main groups of drugs, removing many side signs of the disease. For example, it fights well against nervousness, irritation. It takes a long time to take, but the risk of complications is eliminated for a long time.
With the exception of rare medical cases, almost everyone experiences pain at least once in their life. The nervous system is responsible for them. The unpleasant feeling of pain causes irritation or inflammation of the nerve endings. It can occur against the background of an infection in the body, due to muscle spasm, which squeezes blood vessels, etc. Although often inflammation is only a signal indicating the presence of a serious illness in the body.
Hypothermia, drafts, and trauma are often the causes of illness - these are sources of primary inflammation. Secondary arises against the background of certain diseases.
Symptoms of inflammation of the nerve endings
Before proceeding with the diagnosis and prescribing treatment, the patient should describe his symptoms and sensations to the doctor in as much detail as possible. The main sign of inflammation is pain, the focus of which cannot always be identified independently. It can intensify at night, with any physical activity, even walking, sometimes in the cold.
The second most characteristic sign indicating that there is inflammation of the nerve endings in the body is a burning sensation and tingling in the affected area. Depending on the pathology zone, pain can occur even with minor skin irritations.
In general, all symptoms depend on which area of \u200b\u200bthe body the lesion occurred in. For example, with inflammation of the nerve endings of the legs, the sensitivity of the foot or lower leg worsens. Often, movements in the knee area are severely limited and cause pain at the slightest change in position. In case of eye disease, the pain makes itself felt when the eyeballs move, and vision often decreases.
Inflammation of the nerve endings of the spine
Very sharp pains are accompanied by damage to the nerves of the spine. Infectious diseases of the spine, osteochondrosis, and severe trauma can lead to inflammation.
Sometimes the back area is sharply pierced by acute pain, which can occur as a result of excessive exertion, which often leads to sciatica. Its main symptom is vertebral neuralgia. Symptoms gradually increase as spinal disease progresses. Radiculitis is also often manifested after "advanced" osteochondrosis. It can "settle" in any area of \u200b\u200bthe spine, which leads to constant pain in the back, reminiscent of impulses.
With osteochondrosis, which is the cause of back pain in 90% of cases, degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs occur. When the disc collapses, it extends beyond the spine. Vessels and nerve endings are located around it. If the disc touches them, then the person develops pain syndrome.
Among the main diseases of the spine that provoke acute pain, there are also herniated discs, lumbago, sciatica, scoliosis, and intercostal neuralgia. Of course, this is not the whole list of diseases that can provoke inflammation of the nerve endings. Therefore, you should not self-medicate.
In most cases, a warm woolen scarf or a blanket on the lower back is not enough. An accurate diagnosis can only be made by a doctor who prescribes effective treatment, contributing to a speedy recovery.
Inflammation of the occipital nerve
Inflammation of the occipital nerve leads to frequent headaches. The pain occurs in the back of the head, radiates to the front and sides of the head. It is not uncommon for patients to describe pain sensations similar to those experienced with migraines. The scalp can also become very sensitive to touch. For example, even when trying to comb your hair, you experience unpleasant painful sensations.
By the way, with occipital inflammation of the nerve endings, doctors often face some difficulties. They are due to the fact that it is often difficult at this stage to distinguish inflammation from other causes due to which headaches occur. Therefore, the patient is obliged to describe in as much detail as possible all the symptoms present and honestly answer the doctors' questions.
 If headaches bother you constantly, you should immediately consult a specialist. In this case, it is not enough to take exclusively painkillers, which the patient chooses at his discretion in the pharmacy. Often, doctors carry out complex diagnostics, including computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. This is necessary because sometimes infections, brain tumors, trauma, and lupus can cause secondary occipital neuralgia.
If headaches bother you constantly, you should immediately consult a specialist. In this case, it is not enough to take exclusively painkillers, which the patient chooses at his discretion in the pharmacy. Often, doctors carry out complex diagnostics, including computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. This is necessary because sometimes infections, brain tumors, trauma, and lupus can cause secondary occipital neuralgia.
If the inflammation does not require surgery, the doctor will prescribe a treatment aimed at relieving pain. Drug treatment combined with physiotherapy procedures, massage. In addition, doctors recommend getting more rest. Additionally, they can prescribe a course of anticonvulsants, steroid anti-inflammatory drugs.
Cases where a surgeon's intervention is required to treat a disease are less common. With chronic pain, the absence of positive results from conservative treatment methods, an operation is indicated.
Treating inflammation
Sometimes the inflammation of the nerve endings is so strong that pain occurs even with the slightest irritation of the skin.
In order for the prescribed treatment to be effective, it is necessary to establish the cause that caused the disease. If all the symptoms indicate that an infection has led to the inflammation of the nerve endings, doctors usually prescribe antibiotics in injections. Treatment with antiviral drugs is often required.
In case of decreased blood circulation (ischemia), medications are taken that dilate blood vessels and stimulate their work. If symptoms indicate traumatic neuritis, doctors prescribe pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications. Additionally, a course of injections can be prescribed.
When drug treatment comes to an end, the patient may be referred for physical therapy.
Sometimes a surgeon's intervention is required to free the nerve. The need for surgery arises when there is strong compression or in cases where the nerve grows in the wrong direction.
Inflammation of the nerve endings is often a symptom of serious illness. So neglect painful sensations in the zone sciatic nerve, spine, head or other area of \u200b\u200bthe body is prohibited. You should immediately consult a doctor to relieve discomfort. Regular pain is not a reason for self-medication, which can lead to unpleasant consequences. It is important to find the cause of the pathology and eliminate it with the help of a competent doctor.
Nervus trigeminus - this is the fifth pair of cranial nerves. It consists of three branches and provides sensitive innervation to the face area, including the teeth, and motor masticatory and facial muscles. In dentistry, the following lesions are found:
- Neuralgia is a pathological change in the sheath of the nerve fiber. Acute severe pain is characteristic. It is recognized as the main symptom of other pathologies.
- Neuritis is an inflammation of a nerve that affects its entire structure.
IMPORTANT! A distinctive feature: with neuritis, motor disturbances and loss of sensitivity are observed, with neuralgia - no.
The reasons
Inflammation n. trigeminus - polyetiological disease. Its occurrence is facilitated by:
- Bacterial and viral infections in the organs of the head.
- Injuries (fractures of the bones of the skull, difficult extraction of teeth, incorrect performance of anesthesia or prosthetics). Mechanical violation of the integrity of the nerve leads to its dysfunction.
- Entrapment (compression foreign body, bone, vessel, tumor). The oxygen supply is disrupted to the compressed area, and ischemia is the main condition for necrosis.
- Inflammation in the surrounding tissues (pulpitis, periostitis, periodontal disease).
- Hypothermia and stress reduce immune defenses, which contributes to the rapid spread of infections.
- Intoxication. Poisonous substances (carbon monoxide, phosphorus compounds, mercury, arsenic) are very aggressive to the protective membranes of any organs.
- Allergic reaction. Occurs when prosthetics of teeth with materials that the body rejects.
- Multiple sclerosis. It is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the fiber sheath of the central nervous system. Neurons are replaced by connective tissue, plaques are formed that disrupt the function of the nerve.
The main symptoms
Neuritis of any etiology has a characteristic clinical picture:
- Pain syndrome is the first sign of tissue damage.
Shooting pain, paroxysmal, very strong, lasting up to a couple of minutes. It appears in one half of the face.
IMPORTANT!A dull aching pain may appear, similar to a toothache with advanced caries or pulpitis, which leads to the need to visit the dentist. 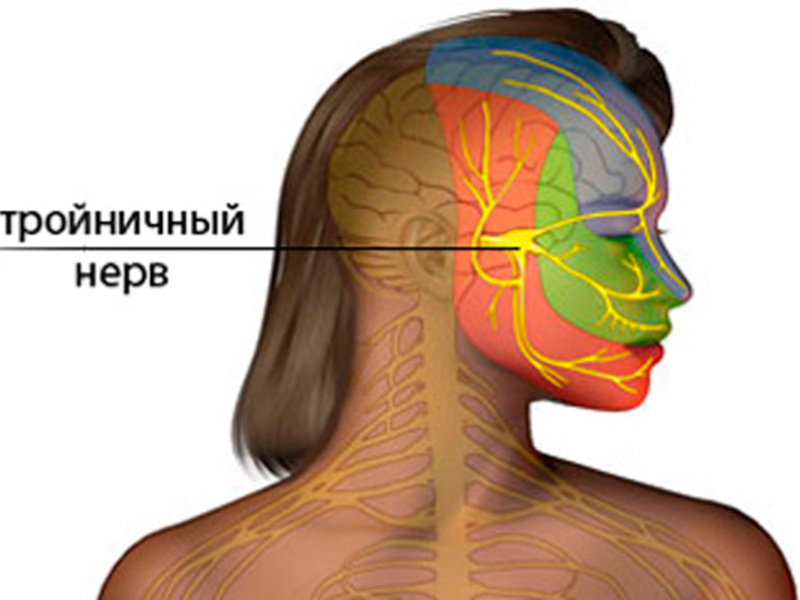
- Redness of the sclera of the eyes and face.
- Increased salivation.
- Lachrymation.
- Runny nose.
- Tremor (twitching) of the facial muscles, similar to a nervous tic. This is due to the overexcitation of motor fibers.
- Narrowing of the eyes on the painful side - spasm of the eyelids.
- Parasthesia (sensitivity disorder). On the affected half, the feeling of creeping, tingling, or, conversely, the skin does not respond to stimuli.
- Mental disorders: irritability, anxiety, apathy, silence, depression, the appearance of a feeling of fear, psychosis. They arise from excruciating and debilitating bouts of pain.
- Asymmetry of the face, peeling of the skin, loss of eyebrows, eyelashes, hair or teeth, weakness of the chewing muscles are signs of trophic failure. They appear several years after the onset of the disease due to a disorder of blood and lymph circulation.
The defeat of the nervus trigeminus affects one face (usually the right). It extends to the second side only in severe pathologies of the brain.
When the trigeminal nerve is chilled, the symptoms are varied, but treatment cannot be postponed!
How is a congested trigeminal nerve treated?
It is easy to get cold, but getting rid of the disease is difficult and long. A set of measures is needed: medicines, physiotherapy and rehabilitation.
Although neuritis pains may be similar to dental pain, it is diagnosed and treated by a neurologist, not a dentist!
Therapy depends on the etiology of the disease:
- In case of infection, bacteria and viruses are destroyed (antibiotics, sulfonamides, interferon, serum, gamma globulin).
- In case of injury, the integrity of the tissues is restored by surgery.
- When pinched, the nerve is released. For ischemia, a vasoactive (vasodilator) agent (aminophylline) is used.
- With hypothermia, you should avoid situations and places where you may be blown out.
- With weak immunity, it is necessary to drink vitamin courses. After consulting a doctor!
- When intoxicated with medicines (rheopolyglucin, sodium thiosulfate, antidotes) and medical equipment accelerate the elimination of toxic substances from the body.
- In case of allergies, the contact of the allergen with the tissues is eliminated.
- With multiple sclerosis, neurologists use an individual approach. The main task is to transfer the disease into remission and ease its course.
- For neuritis caused by improper dental prosthetics, treatment is carried out orthopedic.
IMPORTANT! Careless manipulation of instruments by the dentist can injure neurons and lead to more serious consequences.
Medicines
Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating pain and the underlying causes of the disease:
- Antiepileptic (anticonvulsant) drugs: carbamazepine, lamotrigine, phenytoin, gabapentin, clonazepam, sodium valproate, stashchepin. They reduce the excitability of neurons, as a result, the pain subsides.
- Muscle relaxants: baclofen, midocalm. Elimination of muscle spasm, analgesic effect.
- B vitamins. Promote the regeneration of the nerve sheaths.
- Unsaturated fatty acids (Omega-3). Material for the restoration of neuron myelin.
- Sedatives: glycine, chlorpromazine, mitriptyline. Calming and antidepressant effect, improves sleep.
- Antihistamines (antiallergic): diphenhydramine, pipalfen. Suppress the immune response, enhance the effect of antiepileptic drugs.
- In case of severe and severe pain, the doctor may prescribe narcotic analgesics: forphin, sodium oxybutyrate.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy - therapeutic and rehabilitation methods based on the use of natural and artificially created natural factors on the human body.
Types of physiotherapy:
Physiotherapy
After the main therapy, a complex of exercise therapy is performed for faster rehabilitation of patients.
CAUTION! If there are signs of intoxication or soreness, it is worth postponing with therapeutic exercises. Perform exercises only after consulting a doctor!

Folk remedies
You can also cure a chilled nerve at home. For this, there are the following recipes and methods:
- Pork fat and dried lilac leaves. These ingredients are mixed in a 1: 1 ratio. The resulting ointment is rubbed up to 5 times a day.
- The horseradish root should be grated. This mass is put into gauze and the resulting warming compress is applied to the sore spot.
- 1 tbsp. a spoonful of crushed dry millennial add 200 ml of boiling water. Take orally 1 tbsp. spoon 3-4 times a day before meals.
- 1 teaspoon of dried chamomile flowers is poured with a glass of boiling water. The liquid is cooled and kept in the mouth until the pain subsides.
- 1 tbsp. a spoonful of mint is boiled in a liter of water for 10 minutes. When severe pain drink 100 ml of broth in the morning and evening.
IMPORTANT! You cannot do cold compresses on your face, this will aggravate the pathological process.
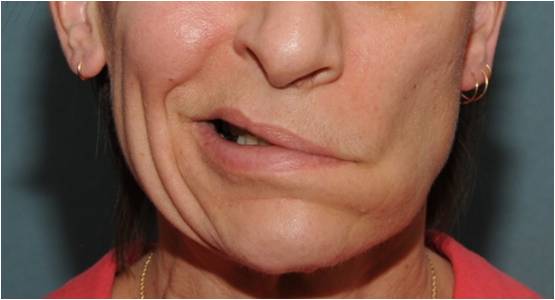
Possible complications and consequences
Before using folk recipe, it should be remembered that these are only auxiliary methods of therapy and a visit to the doctor is MANDATORY in order to avoid complications:
- Psychological problems. Constant exhausting pain traumatizes the human psyche: there are depression, neuroses, tantrums and suicidal thoughts.
- Muscle atrophy, facial numbness.
- Involvement of other organs in the pathological process: visual impairment, hearing loss, conjunctivitis, sinusitis, meningitis.
- Osteoporosis, osteomyelitis.
- Muscle paralysis and the appearance of facial asymmetry.
- Chronic pain.
Prevention of nerve inflammation
- Avoid hypothermia. In cold seasons, it is necessary to warm up (wear a scarf, a hat, in strong wind and frost - a balaclava or its analogues) so as not to chill the nerve and adjacent tissues.
- Timely and competent treatment of infectious diseases.
- Reducing the risk of stress, as they weaken the immune system and disrupt the central nervous system.
- Annual courses of vitamins, as they are needed to build the sheaths of neurons.
- Home self-massage of the face improves muscle blood circulation.
- Strengthening the immune system. Hardening (sunbathing, contrast shower), healthy 8-hour sleep, good nutrition.
- Annual check-ups for people over 50.
- Avoid injury to the bones of the skull.
- Timely admission to the hospital for discomfort in the nervustrigeminus area.
