Chest hurts and fever are quite common complaints of the female half of humanity. , which is accompanied by a temperature of 37 ° C and above, will make any woman worry about her health.
How to understand whether it is worth sounding the alarm and immediately run to the doctor, or what happened is just a variant of the norm. So, the reasons for the rise in temperature, accompanied by chest pains, are discussed below.
Growing up is a difficult period for a girl, when her body is rebuilt, turning from a child to an adult. Strong hormonal surges affect growth, coordination, even character. Due to an increase in the concentration of progesterone and estrogen, active growth of the mammary glands begins. Their ducts lengthen and branch, the glandular tissue grows, the fatty layer accumulates.
Nerve fibers in the glands grow more slowly and often do not keep pace with the growth of the gland, which forces them to be in a tense, tense state, and gives unpleasant sensations to the owner. In adolescence, girls often begin to hurt their breasts and nipples, the sensations may be aching, pulling, burning. In this case, the body temperature can rise to subfebrile, and reach 37.0-37.5 ° C. Sometimes nausea and vomiting are added. These unpleasant sensations are especially pronounced a few days before the onset of menstruation.
Unfortunately does not exist effective treatment this state, since it is the norm and is necessary for the development of the girl. In severe cases, doctors recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and pain relievers to relieve symptoms. Usually, the manifestations of cyclic mastodynia cease or decrease to insignificant by 15-18 years. But sometimes symptoms can return during pregnancy or during menopause.
Lactostasis
Often from nursing mothers you can hear complaints that the chest hurts, and the temperature has risen. Lactostasis, i.e. milk stagnation, is a very common phenomenon, especially in women who have given birth for the first time. As a rule, this leads to:
- improper or too rare attachment of the child
- wearing a tight bra
- traumatic chest compression during sleep
In rare cases, there are physiological features - narrowing of the milk ducts, high density of mother's milk or sluggish sucking of the baby.
If a nursing mother has a sore breast, you should gently massage it, especially the lobes where there is tension or hardening, and try to express milk as much as possible by hand, using a breast pump or by correctly attaching the baby. Launched lactostasis, if an infection enters the chest, can turn into a much more serious disease.

Lactational mastitis
Since small cracks in the nipples are almost inevitable during feeding, it is recommended to pay extra attention to breast hygiene. If a bacterial infection enters through the crack, breast milk is an ideal medium for it to develop and spread. The signs will be:
- a sharp increase in temperature (with lactostasis, it usually stays within the range of 37-38 degrees, in rare cases up to 39, and with mastitis it can exceed 40 degrees)
- redness of the skin of the chest
- strong pain
Mastitis is characterized by a local lesion of the gland, so it should be suspected when one breast hurts and the temperature rises to 37 ° C.
Treatment for mastitis should be started as early as possible, as the infection develops very quickly. If you suspect mastitis, in no case should you give milk to the child, but it must be expressed. In addition, antibiotic therapy should be started. It is better to immediately consult a doctor for the timely selection of the drug and its dosage. Advanced mastitis can lead to the appearance of an abscess and require surgical intervention.
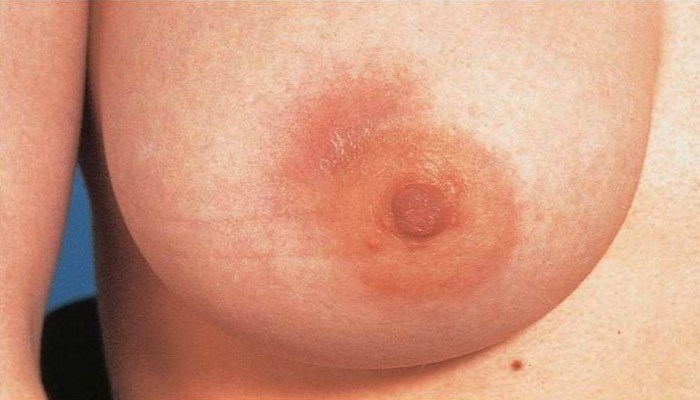
Similar to lactation mastitis in breastfeeding women, inflammation can occur on the breasts of women of any age. The infection can penetrate through damage to the skin, wounds, cracks, breaks. In the vast majority of cases, the causative agent of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus. Mastitis should be suspected even if the temperature is 38 ° C and the chest hurts. And even more so if:
- the temperature jumped sharply to high values \u200b\u200b(39-41 ° C)
- swelling appeared on the chest
- redness
- there is a burning sensation and itching
- strong pain
Affected, as a rule, one mammary gland, left or right. The temperature will help to determine the location of the lesion, the chest literally "glows with heat" in the affected area, the touch is painful. Discharge from the nipples, sulfurous or purulent, may appear.
If you suspect mastitis, you need to see a doctor as early as possible, self-medication can lead to serious consequences. Until the removal of the affected lobe of the breast or death as a result of developing sepsis (bacterial infection of the blood). Antibacterial and detoxification therapy is mandatory, it is important not to self-medicate and not rely on untested methods.
Breast injury
Sometimes, although not often, the breast can be injured. For example, as a result of an accident or traffic accident. At the same time, after an injury, the chest hurts, the temperature rises, and seals can be felt in the chest in places where the fatty tissue of the breast is affected. Over time, necrosis of this adipose tissue occurs. In this case, the affected area hurts a lot, intense itching or burning may be felt.
General intoxication of the body occurs, there may be nausea or vomiting, general malaise, decreased appetite. In place of dead tissue, a scar is formed, while the mammary gland can change shape, a lump may appear or a nipple may be drawn in. These symptoms resemble signs of breast cancer, so a doctor's consultation is necessary to rule out breast cancer.

Breast tuberculosis
This rather rare disease occurs, most often, as a secondary lesion in women who have been suffering from pulmonary tuberculosis for a long time. Should alert:
- change in the shape of breasts
- the appearance of sores on the skin
- aching or bursting pain
- pulmonary symptoms (cough, sputum discharge, chest pain, shortness of breath).
The diagnosis must be confirmed by lung x-ray and biopsy. Treatment is prescribed only by a doctor, and it includes long-term (from a year or more) complex therapy, supportive therapy and, if possible, medications that relieve symptoms.
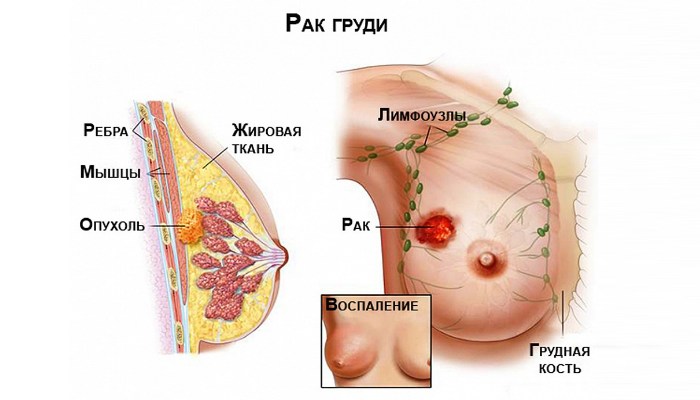
Breast oncology
In recent decades, very sad statistics of women with breast cancer have developed in our country. Often women do not pay attention to disturbing symptoms until it is too late. You should consult a doctor if:
- chest hurts
- temperature 37-38 ° C
- the shape of the breast has changed, the left and right mammary glands are asymmetrical
- nipple retracted
- inside or outside the bump sticks out.
In this case, there may be no pain at all, but there may be a variety of pain - shooting, aching, burning, stabbing pain.
Chest pain is one of those symptoms that cannot but attract attention. Up to 60% of women regularly face this problem, experiencing painful sensations of varying duration and intensity. Often they are accompanied by an increase in body temperature and general malaise, which prompts patients to not at all bright thoughts.
If the pain is accompanied by an increase in body temperature - urgently consult a doctor!
What should you beware of when you have breast pain and fever? What symptoms should you see a doctor immediately? This article describes five causes of chest pain that can be accompanied by a febrile reaction. Some of them are completely harmless and are associated with changes in hormonal levels, while others require immediate medical care.
 Puberty is a special period that is rich in all sorts of surprises, including unpleasant ones. Cyclic mastodynia, or regular pain in the breasts and nipples during menstruation, is one of them.
Puberty is a special period that is rich in all sorts of surprises, including unpleasant ones. Cyclic mastodynia, or regular pain in the breasts and nipples during menstruation, is one of them.
During puberty, the child's body is reconstructed to an adult "mode of functioning", and this is primarily due to the establishment of the correct balance of sex hormones. This is not achieved immediately: the endocrine system takes a very long time to put itself in order, which manifests itself in various symptoms. Teenage aggression, irritability, skin problems, nausea, sweating are all just flowers compared to cyclical mastodynia.
Against the background of an uneven increase in the concentration of estrogen and progesterone in the blood, increased breast growth occurs. The end sections of the mammary gland branch and increase in size many times, its ducts lengthen, and the fatty layer accumulates. Everything would be fine, but nerve fibers do not always keep pace with such rapid growth. They seem to be taut and constantly irritated, which causes a burning, stabbing or aching chest pain.
The situation deteriorates markedly just before the onset of menstruation. At this time, the highest concentration of prolactin is observed in the blood, the terminal sections of the mammary gland are maximally expanded, and the nerve fibers are stretched to the limit. The pain in the chest becomes unbearable, which in especially severe cases is accompanied by an increase in body temperature. There may be a burning sensation in the chest and nausea. Working capacity is completely lost, the girl is sick, and pain becomes the only filling of her life.
As a rule, immediately after the onset of menstruation, the clinical picture becomes much better. Unfortunately, there is no effective treatment for cyclic mastodynia that can remove all symptoms. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which are usually prescribed for headache and toothache, can alleviate the condition, but their effect is not sufficiently pronounced. It is encouraging that for most girls, the cyclical mastodynia goes away on its own after establishing a clear cycle. Then the temperature, nausea, burning and pain in the chest go away.
Traumatic damage to the breast is an uncommon situation. Strange as it may sound, but when falling on ice, many women would prefer to break an arm or a leg rather than painfully hitting their chest. Despite this, the mammary gland is not always protected from injury, and it can be seriously damaged in the following situations:
- falling face down;
- road traffic accidents and other accidents;
- collapse of buildings and stay under the rubble;
- mine blast injury;
- street assault and other accidents.
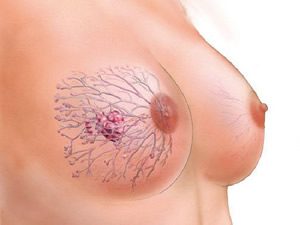 Regardless of the mechanism of injury, damage occurs to the adipose tissue that makes up most of the breast. After some time, this non-viable tissue disintegrates - fatty necrosis. In this case, there is intense pain in the chest, soreness when feeling, the body temperature often rises, especially when the microbial flora joins. Many patients feel sick because the decay products of injured tissue have a toxic effect on the body.
Regardless of the mechanism of injury, damage occurs to the adipose tissue that makes up most of the breast. After some time, this non-viable tissue disintegrates - fatty necrosis. In this case, there is intense pain in the chest, soreness when feeling, the body temperature often rises, especially when the microbial flora joins. Many patients feel sick because the decay products of injured tissue have a toxic effect on the body.
Subsequently, the area of \u200b\u200binjury is replaced by scar tissue, due to which the chest itches, a burning sensation appears, a lump forms or the mammary gland changes its shape. The skin of the breast becomes lumpy, the nipple is often retracted, which can mimic cancer. Often, even in the long-term period of injury, there may be a burning sensation and pulling pain, especially in the areola and in the area of \u200b\u200binjury. The bump does not always disappear. Sometimes it remains, representing a subcutaneous scar of connective tissue.
The diagnosis of breast trauma and fatty necrosis is difficult to make. For this, it is extremely important to know the history. In other words, the patient should describe the circumstances of the injury to the doctor. Treatment of this condition is complex and includes both medical methods and surgical intervention.
Lactational mastitis
Most common reason pain in the mammary gland, in which the body temperature rises, is lactational mastitis, or breast inflammation. For the development of this disease, a combination of several factors is needed:
- Stagnant milk (mom refuses to breastfeed or does not express milk).
- Cracks and other injuries to the nipple and areola.
- Lack of breast hygiene.
- The presence of diseases in a woman, which are accompanied by a decrease in immunity and a general weakening of the body.
Milk that stagnates in the mammary gland is a very favorable environment for the development of pathogenic flora. It enters the ducts and end sections of the gland through the entrance gate, the role of which is played by the damaged nipple. As a result, inflammation occurs in the gland tissue, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Intense pain, which may be burning, bursting, pulling and throbbing;
- Swelling of the chest;
- Redness of the breast skin;
- Discharge from the nipple, including purulent;
- Sometimes the chest itches, possibly burning.
- Symptoms of a systemic inflammatory reaction: body temperature rises, often nausea, sweating, weakness and general malaise appear.
 Typically, mastitis affects only one breast. Not to mention that it is better not to reach such a state at all, it is important not to start the disease and consult a doctor as soon as possible. If you postpone the consultation of a specialist, then an abscess (abscess) will form in the breast tissue, the condition will be even worse, and this is fraught with the development of sepsis.
Typically, mastitis affects only one breast. Not to mention that it is better not to reach such a state at all, it is important not to start the disease and consult a doctor as soon as possible. If you postpone the consultation of a specialist, then an abscess (abscess) will form in the breast tissue, the condition will be even worse, and this is fraught with the development of sepsis.
Treatment for mastitis necessarily includes powerful antibacterial and detoxification therapy. It allows you to reduce the manifestations of intoxication syndrome (weakness, sweating, nausea). The baby is temporarily transferred to artificial feeding, and mothers are provided with regular expression of infected milk from the inflamed breast. When an abscess appears that looks like a lump in the thickness of the breast, surgery is required.
Breast tuberculosis
Tuberculous lesions of the mammary gland are extremely rare, and precisely because of this, it is very poorly diagnosed. In the overwhelming majority of cases, this disease develops in women who have long-term pulmonary tuberculosis. The defeat of the mammary gland is secondary and indicates the neglect of the condition, as well as inadequate treatment.
Breast tuberculosis is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Aching, bursting, or pulling pain in the chest.
- Deformation of the mammary gland: lumps, retractions, change in the shape of the nipple.
- Ulcers may develop on the skin of the chest.
- Unusual nipple discharge.
- Lung symptoms: cough, shortness of breath, pain in chestthere may be hemoptysis.
- Signs of general intoxication: body temperature rises, appetite disappears, sweating appears, general malaise, and often nausea.
 Diagnosis of breast tuberculosis is based on chest x-ray and breast biopsy. Treatment is long-term (up to 1 year or more) and includes a combination of several heavy drugs. Sometimes surgery is required up to the removal of the breast.
Diagnosis of breast tuberculosis is based on chest x-ray and breast biopsy. Treatment is long-term (up to 1 year or more) and includes a combination of several heavy drugs. Sometimes surgery is required up to the removal of the breast.
Additional use of symptomatic therapy is possible if a woman is worried about burning, pain, nausea, or other symptoms of the disease.
Mammary cancer
Unfortunately, in our country the situation with breast cancer is rather depressing. Surprisingly, many women start their illness, which has extremely striking external manifestations. Because of this, the prognosis for life is significantly worsening, and patients go to the doctor at the later stages, when nothing can be done.
A serious suspicion of breast cancer should arise if the following symptoms are observed:
- The nipple is retracted, the shape of the breast has changed;
- The chest hurts, and the pain can be burning, pulling, aching, stabbing - in other words, of absolutely any nature;
- An unusual lump is felt in the thickness of the chest;
- Deteriorated appetite, weight loss, nausea, general malaise, subfebrile temperature (37,0 – 37,9);
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Although even benign breast diseases can have such a clinical picture, timely detection of breast cancer is the surest way to a speedy recovery and a life without suffering.
Many patients who have ever had an excruciating seizure fear a recurrence. In this case, they are ready to associate every manifestation of chest pain with this disease.
What diseases are fatal?
But there are more formidable diseases, which, despite the fact that their course is not accompanied by such acute pain, can be fatal;
- For example - pneumonia. Let's start with the fact that neuralgia is uncharacteristic. Therefore, in the case of fever associated with chest pain, the first thing to do is to hospitalize the patient with a chest x-ray;
- Exudative and dry pleurisy. They can be both a complication of pneumonia and arise independently and even accompany malignant tumors. Diagnostics and treatment are carried out by a pulmonologist, based on the results of X-ray and computed (or magnetic - resonance) tomography;
- Pericarditis. The accumulation of fluid in the cavity of the heart shirt can speak of a wide variety of diseases - from rheumatism and lupus erythematosus to tuberculosis and heart disease. Symptoms also do not imply an increase in temperature, but if it happened, a preliminary conclusion can be made about the septic nature of the process. I need an urgent consultation with a cardiologist, ECG recording and hospitalization in a specialized hospital.
It should be noted that in the case of both pleurisy and pericarditis, it is imperative to carry out a puncture in order to analyze the resulting fluid and the possible obtained cellular composition.
So, for example, if the liquid is cloudy, contains a large amount of protein, fibrin, leukocytes predominate in the cellular composition, this will indicate inflammation, and the liquid will be called exudate.
If the liquid is transparent, with scanty content, it may be a passing "aseptic" transudate.
How do acute symptoms of disease occur?
Recently, effusion pleurisy occurs in young motorists, who, carried away by the "fashionable" car sound, put powerful subwoofers in the trunk and interior. Low frequencies irritate the parietal and visceral pleura, and reactive pleural effusion occurs. In the case of a secondary infection, purulent pleurisy occurs, which needs drainage and flushing of the pleural cavity with antibiotic solutions.
Also, the penetration of the stomach ulcer with its high and atypical location, or even perforation, is not excluded. In this case, the pain will radiate to the chest, and the symptoms of fever and intestinal paresis (absence of stool, increased gas formation) will indicate a serious catastrophe in the abdominal cavity.
You should also not drag out for time and think that everything can be resolved "by itself." Every lost hour can cost health, and in some cases, life. That minimum of research - general analysis blood count, ESR, chest x-ray, ECG and abdominal ultrasound can help save a person.
Therefore, when chest pain and fever appear, you need to call a doctor and carry out the necessary examination, because neuralgia is the least of evils that can happen to you.
According to statistics, about 16% of lactating mothers, especially from among primiparas, suffer from advanced stagnation of milk in the ducts (lactostasis) and, as a result, mastitis.
Therefore, if a woman's chest hurts and the temperature rises sharply to 38 - 39 ° C, urgent action is needed.
Despite the fact that modern medicine successfully treats mastitis, it is advisable to eliminate the possible root causes of this unpleasant and dangerous disease. In the treatment of mastitis, accurate diagnosis is important, since its symptoms are similar to lactostasis, but the treatment of pathologies is fundamentally different.
Etiology
If, while breastfeeding, the chest hurts and the temperature rises suddenly, the cause of this phenomenon may be neglected lactostasis or mastitis.
Reasons for lactostasis:
- the structure of the breast, provoking the formation of a milk plug;
- squeezing the breast with a hand while feeding, sleeping on one side, feeding in an uncomfortable position, wearing tight clothes, etc.;
- prolonged pumping;
- stress causing a spasm of the milk ducts;
- chronic fatigue;
- high fat content of milk;
- using a pacifier that changes the baby's sucking technique;
- hard work with monotonous hand movements.
Lactostasis sometimes develops into mastitis.
Factors provoking mastitis:
- irregular feeding or feeding at intervals of more than 2 hours;
- persistent milk residues in the breast;
- cracks in the nipples through which the infection penetrates;
- anemia, decreased immunity;
- violation of hygiene standards and poor nursing breast care;
- tight, tight bra;
- hypothermia;
- improper feeding of the baby, poor, incomplete pumping;
- viral infections;
- history of breast pathology;
- complications during delivery, suppuration.
What is the difference between lactostasis and mastitis
If a nursing woman has chest pain and fever, this condition can be caused by both lactostasis and mastitis.
Milk stagnation, especially in primiparous, can be difficult to distinguish from the onset of mastitis.
Their symptoms are largely the same, but there are differences.
A sign of mastitis is a sharp rise in temperature up to 39 ° C against the background of swelling of the nipple, chills, chest pain.
With lactostasis, the duct is clogged, the thickening and redness of the skin is local, the temperature is low. If this condition lasts a week or more, mastitis may develop.
Types and symptoms of mastitis
 With mastitis, the chest hurts, the temperature is 38 ° C and above, the symptoms progress quickly. If not treated in any way, one stage can turn into another in literally 3 days.
With mastitis, the chest hurts, the temperature is 38 ° C and above, the symptoms progress quickly. If not treated in any way, one stage can turn into another in literally 3 days.
Varieties of mastitis
- Serous.
- Infiltrative.
- Purulent.
Not typical for the serous variety heat, the breast enlarges and becomes painful.
Infiltrative mastitis is manifested by seals, on palpation of which unbearable pain is felt. The temperature is very high, the skin on the chest turns red, becomes hot and elastic.
With a purulent form, the chest swells greatly, increases, reddens at the site of the inflammation, it hurts unbearably and with light touch. Migraines and weakness occur. Pus is noticeable in the milk, the lymph nodes in the armpits are enlarged. The temperature can reach 40 ° C, and then drop, fluctuating.
With unilateral suppuration, you can feed the baby, but only with a healthy breast, since the bacteria can easily be passed on to the newborn.
Diagnostics
When the chest hurts and fever with hv, according to some signs (red painful spots on the chest, high temperature), you can self-diagnose mastitis. But at an early stage, it is difficult to distinguish it from stagnant milk.
If you suspect mastitis, you cannot start treatment on your own without consulting a gynecologist and laboratory data. Mastitis should be treated as soon as possible, and without identifying a specific pathogen it is impossible to choose the right one medicinal product or folk remedy. Also folk methods not designed for quick effect.
Diagnostics includes examination by a mammologist, ultrasound, blood test, breast milk.
If the diagnosis of mastitis is confirmed, antibiotics will be prescribed on the basis of the studies, including some modern means that can be used for feeding.
Why is self-medication dangerous?
 Self-medication is dangerous by incomplete getting rid of the infection, when the symptoms are temporarily stopped, while bacteria continue to divide and inflammatory process flashes with renewed vigor. The application of cabbage leaves and other remedies that may be helpful in treating lactostasis are inappropriate for the treatment of mastitis. Home remedies are slow-acting and ineffective for severe infections. As a result, the disease will progress.
Self-medication is dangerous by incomplete getting rid of the infection, when the symptoms are temporarily stopped, while bacteria continue to divide and inflammatory process flashes with renewed vigor. The application of cabbage leaves and other remedies that may be helpful in treating lactostasis are inappropriate for the treatment of mastitis. Home remedies are slow-acting and ineffective for severe infections. As a result, the disease will progress.
Therefore, when the chest hurts and the temperature rises even slightly during feeding, the algorithm of actions should begin with a trip to the doctor.
Therapy
The basic principle of mastitis therapy is regular and complete pumping. For this purpose, it is convenient to use a high-quality expensive breast pump or seek help from your husband.
Since the newborn can be breastfed at an early stage, breastfeeding should be started on the diseased breast, even if there is pain. Before the process, drop 4 drops of "Oxytocin" under the tongue to enhance the outflow of milk and eliminate spasms. You can also take a warm (but not hot) shower and gently massage your breasts in light circular movements towards your nipples. Then you need to express the remaining milk by hand and using a breast pump until the feeling of heaviness disappears. After the procedure, apply ice wrapped in cellophane and cloth to the chest for 15 minutes.
The actions must be repeated every 2 hours, including at night. In this case, it is important to correctly apply the baby to the breast - so that the lower lip is in the place of hardening.
Taking most of the antibiotics needed to treat advanced mastitis is a contraindication to feeding.
With normal milk stagnation, drug therapy may not be required.
Particularly severe cases of purulent mastitis are treated only promptly, so it is important not to start the pathology.
Medicines
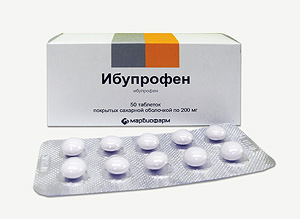 To bring down the temperature from 38.5 ° C, antipyretics based on paracetamol or ibuprofen are shown.
To bring down the temperature from 38.5 ° C, antipyretics based on paracetamol or ibuprofen are shown.
In the presence of cracks in the nipples, local therapy with Purelan-100, Bepanten and other means is used.
Early diagnosis and timely treatment of mastitis avoids taking antibiotics.
Prevention
Prevention of mastitis and lactostasis includes:
- local hardening of the nipples, for example, daily washing the breasts with cool water, rubbing with a coarse towel, starting from the gestation period;
- washing hands and breasts before feeding;
- correct attachment to the breast of the newborn;
- timely elimination of cracks in the nipples - a source of penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the mammary glands;
- feeding in the first month at the first request of the child;
- use of comfortable bras without hard parts cutting into the body.
Nursing should avoid drafts and blows to the chest. If there is a history of mastitis, it is recommended that you express milk after each feed (but this is a controversial point). Therefore, preventing milk duct blockages lies in correct, frequent and regular feeding. In the presence of stagnant processes in the chest, you should immediately consult a doctor so that lactostasis does not develop into mastitis.
During breastfeeding a nursing mother may have breast problems. Especially often young mothers who have had their first child suffer from this, since before this event there was no experience of latching a baby to the breast. When the mammary glands cause a woman discomfort, pain, and a rise in temperature occurs, this indicates that the disease begins: lactostasis or mastitis. How do they differ, and how to deal with these diseases?
There are many reasons that can lead to lactostasis or mastitis. It is important to understand in time what you are doing wrong in order to fix it, or to check if you are at risk, so as not to bring the disease to a severe form.
The chest hurts and the temperature rises suddenly due to:
- chronic stress, fatigue, lack of sleep;
- increased fat content of milk;
- long pumping;
- uncomfortable feeding posture;
- sleeping on your stomach or on one side;
- changes in sucking technique when the baby starts using the pacifier;
- anatomical structure of the breast;
- lack of a feeding regime (milk remains in the breast);
- wearing tight and uncomfortable underwear;
- hypothermia;
- improper attachment of the newborn to the mammary gland;
- lack of hygienic breast care;
- childbirth problems;
- viral infections, lowered immunity, lack of hemoglobin in the blood;
- cracked nipples.
All of these problems can lead to diseases that are severe. If you start everything, then there is a chance that a woman will be in a hospital with an infection, then the baby will be without breast milk.
Lactostasis
Chest pain and temperature speak primarily of lactostasis. This is called stagnation of milk in the breast with blockage of the milk ducts. This attack manifests itself in the first months of breastfeeding, when the production of breast milk has not yet been established, it arrives in the amount that the newborn does not need.
Main reasons:
- improper seizure of the nipple by the baby when feeding;
- incorrect body position during sleep and when feeding.
To prevent the onset of lactostasis, while still in the hospital, contact your medical staff for information on how to breastfeed properly. If this facility does not provide you with the assistance you require, you can always ask a feeding specialist.
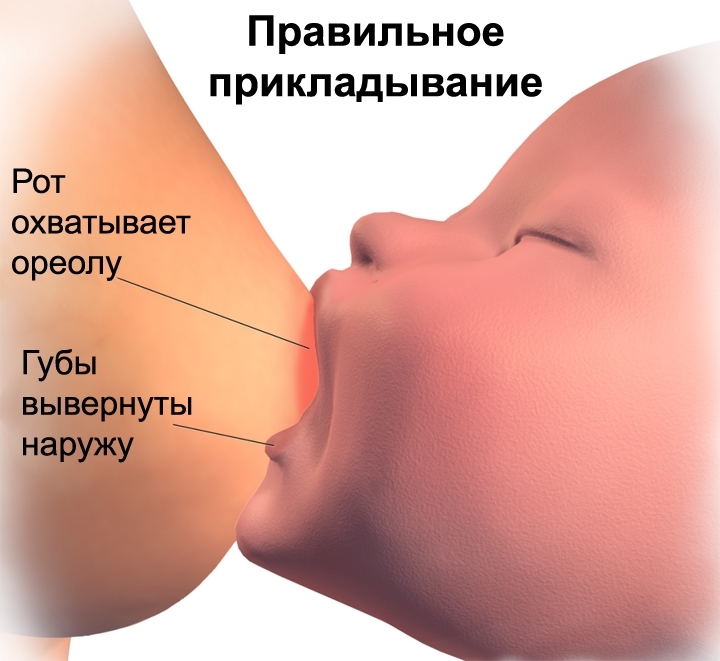
Firstly, the correct feeding position is considered to be when the baby grasps the nipple and areola entirely, the mouth is wide open, and the lower lip is turned down. At the same time, a nursing mother should not feel pain. Secondly, wear a comfortable bra that will not pinch your breasts. Do not skimp on new underwear, what you wore before pregnancy will not come in handy in the near future, because your breasts are now increased by a size or more. Third, try to maintain a feeding regimen to improve milk production.
When the chest hurts and the temperature of 37 ° has been holding for several days, and constant expression and frequent latching of the baby to the breast do not alleviate the situation, but, on the contrary, adds more discomfort, contact your doctor at the antenatal clinic. Experts will be able to give the necessary recommendations: what ointment or gel you can use, how to massage your breasts, and if necessary, prescribe medications that will not interrupt breastfeeding.

Mastitis
If a nursing breast hurts and the temperature rises to 39 °, then this indicates the transition of lactostasis to a more severe form - mastitis.
In the course of the disease, it happens:
- serous;
- infiltrative;
- purulent.
Serous - this is the first stage of mastitis, which is easier to deal with, you need to urgently seek help from a specialist who will prescribe the necessary treatment.
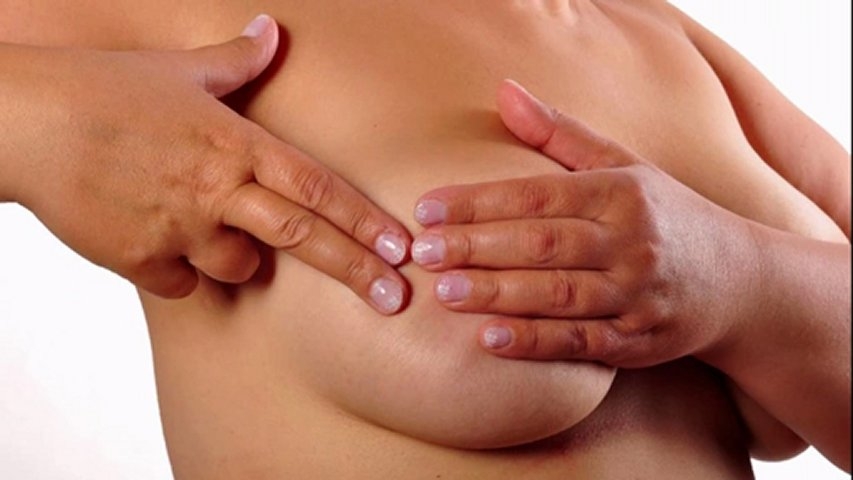

When the chest hurts and the temperature with HB are not the only symptoms, and to this are added thickening in the chest, redness of the skin, difficulty in expressing, then mastitis has passed into the next - infiltrative form of the disease. At this stage, it is very important to urgently see a doctor in order to correct the situation.
It is important not to allow a purulent form to develop, in which a fever of 39-40 ° will be kept, unbearable pain will occur when feeding and even a light touch, cyanotic skin areas will appear where milk stagnation has occurred, pus will be released from the nipples with milk. It is required to immediately stop feeding, call an ambulance.
In the hospital, a nursing woman will be cured with antibiotics; you will have to refuse feeding for the period of treatment.
Diagnostics
It is very difficult to independently distinguish mastitis from lactostasis, because the symptoms are similar (chest pain and temperature up to 38 °). However, with mastitis, red patches of skin appear on the chest, the chest is thickened, swollen, and even a slight touch or friction causes severe pain.
You should not diagnose yourself without visiting a doctor and resort to folk remedies... At best, you will waste time; at worst, you will make the situation worse. To make a diagnosis, the mammologist will refer you to a blood and breast milk test, an ultrasound of the mammary glands.
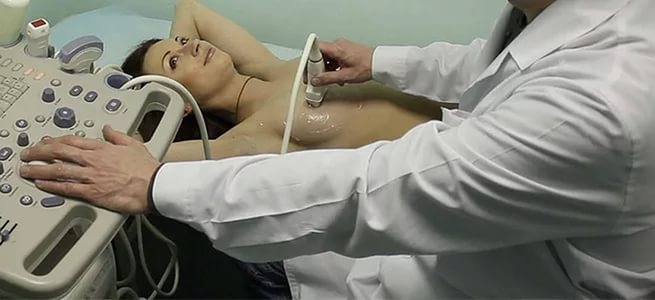
Treatment
Do not treat symptomatically: by drinking pain relievers, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs, you will not cure mastitis, but only put your health and children's health at risk. The bacteria will begin to divide in an enhanced mode, after a while the pain will flare up with renewed vigor.
When the chest hurts and the temperature rises during breastfeeding, you should immediately visit the doctor in the antenatal clinic. The doctor will prescribe the necessary treatment, give recommendations on how to behave when feeding, explain what drugs can affect the child. Now there are many medicines that can heal the breast without weaning the baby from it.
The main principle is to express milk from a diseased breast as often as possible, even if the breast hurts and the nursing woman has fever. Purchase a high-quality breast pump for this procedure, express after each feeding (every two hours) the remains until you feel the feeling of heaviness in the mammary gland disappear. Then apply ice, wrapped in a bag and cloth.
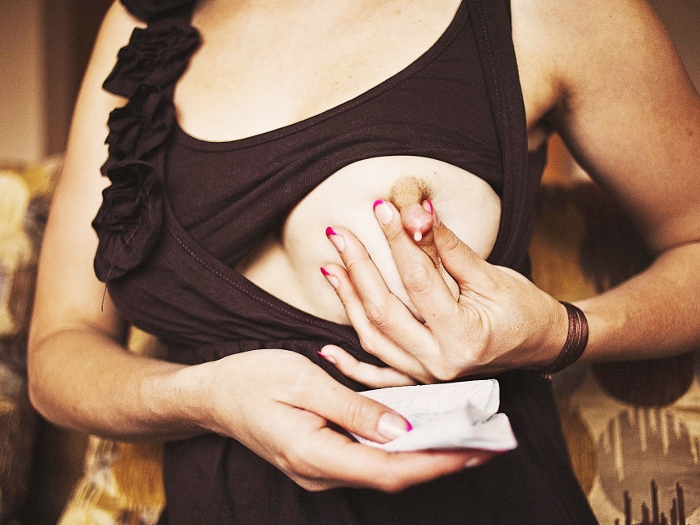

You can also massage your breasts in a warm shower, moving in a circular motion towards your nipples.
If a specialist has prescribed antibiotics, then breastfeeding should be suspended until complete recovery. You can not feed either a diseased mammary gland or a healthy one! When a woman with mastitis has a fever above 38 °, you can take an ibuprofen tablet, cracks on the nipples are treated with Bepanten. With such a disease, sometimes a cabbage leaf is applied to the diseased breast, it will relieve inflammation, but only in the initial stages of mastitis. If everything is started, the doctor may prescribe surgical treatment.
Prevention
In order to prevent stagnation of milk in the milky lobules, you need to follow some rules.
- Wear comfortable underwear that won't be tight or tight.
- Take care of your breasts, starting from pregnancy, temper it by washing it with cool (but not cold!) Water, wiping it off with a coarse towel. Before feeding, carry out hygiene procedures with the breast, wash your hands, and do the same after feeding the baby.
- Don't expect cracks to heal on their own. Now there is a large selection of ointments and gels that will cure this ailment in a short time.
- Latch the baby correctly to the breast, in the first month of his life, let us breastfeed on demand, in order to then build a regimen and establish the flow of milk.
- Try not to be in a draft, during breastfeeding, women's breasts are especially sensitive, it is easy to get cold.

If you follow these simple rules, then you will not learn from your own experience what lactostasis and mastitis are!
Video
How to get rid of lactostasis and avoid mastitis, you will learn from our video.
