Eustachitis is a pathology associated with impaired ventilation and inflammation of the middle ear, which results in hearing loss. Eustachian tube inflammation, treatment and symptoms which we will now consider is considered the initial stage of catarrhal otitis media.
Eustachian tube inflammation symptoms
This is the name of the canal in the ear, which connects the nasopharynx to the tympanic septum. The job of the Eustachian tube is to exchange air in the middle ear when swallowing. The drainage function of the Eustachian tube is to remove various secretions from the middle ear. When swallowed, fluid from the middle ear is pumped into the nasopharynx. Killing bacteria with the produced mucus is also the job of the Eustachian tube.
The main symptoms of inflammation of the Eustachian tube:
Hearing impairment
Feeling of stuffiness in the ears
Feeling of water in the ears as symptoms of inflammation
Painful sensations as symptoms of inflammation
Noise in the ear
As a result of inflammation, the mucous membrane thickens, and, as a result, the lumen decreases, and this leads to a decrease in ventilation of the tympanic cavity and a decrease in pressure there. Due to a decrease in pressure, the membrane begins to be drawn into the tympanic cavity, which causes discomfort in a person.
Eustachian tube inflammation symptoms different types
Inflammation of the Eustachian tube occurs in acute and chronic form.
Acute inflammation of the Eustachian tube it is customary to call the initially developed disease. Most often, the symptoms of inflammation are caused by the action of pneumococci and streptococci, staphylococci and other infectious agents are less likely to cause it. In the absence of proper treatment, inflammation of the Eustachian tube can become chronic. Typical symptoms of inflammation of the Eustachian tube:
- feeling of tinnitus,
- decreased hearing quality,
- sensation of water pouring in the ear when turning and tilting the head.
Pain symptoms are practically not typical for the acute form of the disease, the general state of health suffers weakly, and the temperature does not rise.
The acute phase of inflammation occurs unexpectedly, congestion, noise in the ear, a feeling of fluid transfusion, hearing loss. If the inflammation of the Eustachian tube lasts long enough, it becomes chronic.
Chronic Eustachian tube inflammation develops as a result of improper treatment or its complete absence in acute eustachitis. In the chronic form of the disease, there is a persistent decrease in the diameter of the auditory tube, the eardrum is pulled inward. The permeability of the Eustachian tube is noticeably deteriorating, the walls stick together, which most negatively affects the quality of hearing. Chronic eustachitis can give rise to such a serious disease as adhesive otitis media, which should be understood as the inflammatory process of the middle ear.
Inflammation in the Eustachian tube and tympanic cavity is called tubo-otitis.
Eustachian tube inflammation treatment
It should be understood that inflammation of the Eustachian tube is an inflammatory process, and not just a mechanical blockage of the nasopharyngeal lumen of the Eustachian tube, as it can occur with formed tumors or adenoids. That is why the treatment of inflammation is carried out with the use of antibacterial therapy, anti-inflammatory drugs and appropriate immunomodulatory drugs. In addition, to restore hearing function drug treatment inflammation is complemented by methods such as pneumatic massage and ear blowing.
Treatment of inflammation of the Eustachian tube with drugs
When painful processes began in the nose or nasopharynx, the Eustachian tube perceives it instantly. Treatment of inflammation aims to restore the drainage and ventilation capacity of this pipe.
To reduce the swelling of the mucous membrane, drops that promote vasoconstriction are used. To restore the resorption of the inflammatory fluid, warming compresses and physiotherapy procedures are made.
To exclude the possibility of leakage of infected mucus during inflammation, during a runny nose, from the nasopharynx, through the auditory tube into the tympanic cavity, a sick person should not blow his nose too much.
If the nasopharynx and nose have already recovered, but hearing has not recovered and the tube is still not passable, ear blowing is prescribed. This helps remove moisture through the tube into the nasopharyngeal cavity. If an acute process occurs, then one or three procedures are carried out.
Sometimes, to clean the Eustachian tube, special catheters are inserted into the tube and the tympanic cavity, medicinal enzymes that help dissolve the hardened inflammatory fluid. To relieve inflammation, glucocorticoid drugs are administered.
Correct treatment of inflammation of the Eustachian tube can only be prescribed by a doctor, identifying the root cause of the disease and the localization of inflammation. This inflammation is almost impossible to heal without physical therapy, appropriate warming up and massage. The doctor may also prescribe pain relievers and pain relievers, depending on the degree of pain that the patient feels with inflammation of the Eustachian tube.
Why does inflammation of the Eustachian tube occur?
Inflammation of the Eustachian tube can occur for a number of reasons, such as:
The spread of the infectious process from the nasopharynx, nasal cavity
Acute or chronic sinusitis
Inflammation of the Eustachian tube is also called eustachitis or tubootitis. It is regarded as the initial stage of catarrhal otitis media and implies an inflammatory process localized in the Eustachian tube, leading to otitis media. As a rule, it occurs due to the transition of inflammation in rhinitis, sinusitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis.
Reasons for the appearance of eustachitis
The inflammatory process of the Eustachian tube can be considered as a complication of certain diseases. Such pathologies, first of all, include:
- acute respiratory diseases;
- deviated nasal septum;
- benign and malignant neoplasms of the nasopharynx;
- allergy in the acute stage (hay fever, allergic rhinorrhea);
- chronic inflammation involving the tonsils, sinuses, pharynx;
- infections (syphilis, tuberculosis, candidiasis, scarlet fever, chlamydia);
- aerootites;
- mareotitis;
- incorrect blowing out.
In addition, the predisposing factors leading to inflammation of the Eustachian tube include a decrease in the body's natural resistance forces, its reactivity and immune forces in general.
What are the types of eustachitis
In addition to the fact that Eustachitis can be acute or chronic, there are five types of tubo-otitis:
- catarrhal;
- granulation;
- cicatricial;
- atrophic;
- vasomotor.
With predisposing factors, the same catarrhal tubo-otitis is able to transform into purulent otitis media, and will soon be aggravated by the formation of adhesions in the tube.
The clinical picture of the disease
The symptoms of Eustachian tube inflammation are fairly typical. The classic clinical picture of tubo-otitis includes:

The general condition in the form of intoxication, fever and weakness does not appear. When swallowing or yawning, the ear canal expands, which may reduce the symptoms of Eustachian tube inflammation. The chronic process is characterized by a more tangible and persistent hearing loss, with imaginary periods of improvement, alternating with exacerbations. In addition, from the symptoms, a constant feeling of heaviness on the part of the ear and tube involved in the pathological process is added.
Although the symptoms of inflammation of the Eustachian tube are typical, a diagnosis is required to clarify the diagnosis. Mandatory diagnostic measures include:
- otoscopy;
- microotoscopy;
- audiometry;
- manometry;
- diagnostic tests;
- impedance measurement;
- microscopic, bacteriological examination.
If the disease is caused by an allergic factor, then specific allergy tests are performed. As an additional diagnostic method, computed tomography and radiography are used, including in order to determine the root cause.
Treatment methods
Inflammation of the Eustachian tube, its treatment is conventionally divided into two main areas: medication and auxiliary. It is necessary to eliminate the primary focus of infection, if it exists, to remove swelling and inflammation.
Nasal drops are prescribed for constricting vessels (Nazol, Vibracil, Tizin), antihistamines (Diazolin, Suprastin), antibiotic therapy. Together with these drugs, probiotics and antifungal drugs (Fluconazole) are recommended in order to prevent the appearance of candidiasis during the period of antibiotic use. For topical application, Nazivin, Afenoxin, Otipax, Otinum are widely used.
In addition, the otolaryngologist can massage the eardrum, which has a beneficial effect on its condition and speeds up the healing process. During the period of resolution of the disease, the Valsalva maneuver can be used. It consists in the fact that a person should try to make a strong exhalation, with his nose and mouth closed. Through this technique, the pressure of the internal cavities of the pipe is equalized with respect to atmospheric pressure.
Physiotherapy treatments include laser therapy, magnetotherapy and ultra-high frequency therapy. UFO is also used in conjunction with muscle electrical stimulation. 
In herbal medicine for inflammation of the Eustachian tube, many plants are used. These primarily include:
- immortelle;
- sweet clover;
- pine buds;
- nettle;
- dandelion roots;
- eucalyptus;
- yarrow;
- calendula flowers;
- celandine root.
The necessary combination of plants or one thing is selected, infused in a thermos and drunk fractionally throughout the day. Such treatment is auxiliary and does not replace antibiotic therapy and other proposed methods.
Such plants can cause an allergic reaction in the body and intensify the symptoms, therefore, initially it is necessary to try a small part of the infusion and monitor your condition.
If warming up procedures are not prohibited by the attending doctor, then from budget methods you can try to breathe dry steam of potatoes or carry out similar inhalation procedures.
Summarizing
Prevention of inflammation of the Eustachian tube consists in strengthening the body's immune forces, timely treatment of diseases predisposing to this pathology, avoiding hypothermia. In addition, it is imperative to reorganize the foci of chronic infection.
To strengthen the general condition of the body, it is necessary to correct nutrition, enrich the diet with necessary vitamins and minerals, and a sufficient amount of fruits and vegetables. Dosed physical activity, at least three hours a week, also strengthens the immune system and has a beneficial effect on human health.
Quitting bad habits improves blood circulation and microcirculation. Timely appeal for medical help eliminates the aggravation of the infectious process and prevents complications such as inflammation of the Eustachian tube.
To maintain the health of the ears, it is also necessary to avoid hypothermia, and during epidemics, rinse regularly nasal cavity saline solutions, focus on prevention and vitamin complexes, especially vitamin C.
You can also use chewing gum, carrots, or an apple to speed up the treatment. Due to frequent chewing and increased work of the lower jaw, the accumulated fluid in the auditory tube is quickly evacuated. In some cases, you can resort to catheterization of the auditory tube and the introduction of drugs there.
Closed. At the moment of swallowing food, due to the function of certain muscles located in the soft palate, the Eustachian tube opens and facilitates the penetration of air into the middle ear. This is the constant aeration of this area.
If aeration is disturbed for some reason, then the atmospheric pressure exceeds the pressure inside the eardrum. As a result, her position changes, she becomes drawn in, approaches the wall of the promontorium. Inflammation of the Eustachian tube occurs, the symptoms, the treatment of which are described in this article.
The cause of the disease
All diseases that are accompanied by swelling of the mucous membrane and catarrhal changes in the nose and nasopharynx are able to cause simultaneous inflammation of the Eustachian tube, the treatment of which should be started in a timely manner.
Pathology is provoked by the following reasons:
- runny nose, flowing in acute or chronic form;
- hypertrophic process in the posterior ends of the inferior shells;
- the presence of adenoids;
- neoplasms in the nasopharynx;
- often recurring sore throat;
- hypertrophic process in the tonsils, which can cause secondary pathological changes;
- defects;
- the presence of anterior or posterior tamponade with nosebleeds after surgery.
Usually, tubo-otitis is caused by staphylococci or streptococci. In children, the disease is more often provoked by pneumococci, as well as diseases of a viral nature.
Infection of the nasopharynx spreads to the Eustachian tube, and as a result, its patency is sharply reduced.
If the patient has a predisposition to allergies, swelling of the middle ear and increased secretion, then the risk of the onset of the disease increases significantly. All manifestations of the pathological process depend on the form that it has taken. Inflammation of the Eustachian tube, which is treated by a laryngologist, can be both acute and chronic.
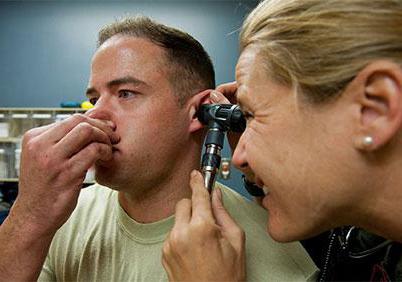
How does the acute form manifest
The acute form, as a rule, develops against the background of a viral lesion of the body, a cold, which inflames the nasopharynx. With the process proceeding in an acute form, the patient notes a stable general state of health. The temperature indicator usually does not exceed 38 ºС. No intense pain is felt. The patient may complain of hearing impairment, nasal congestion, increased hearing of his own voice (feeling as if there is an echo), seeming water overflow in the ear, constant noise.
On examination, the edema of the auditory tube is revealed, the narrowing of its lumen, the mucous membrane is irritated. A closed one provokes a decrease in pressure and expansion of blood vessels, the walls of which become thinner. This causes blood to ooze through the capillaries.
How does the chronic course of the disease manifest?
If in the acute form all the symptoms are temporary and after a while they cease to bother, then in the chronic course they are persistent. Chronic disease is characterized by atrophy in the mucous membrane of the tympanic membrane and membrane. The membrane becomes cloudy, necrosis may form.
In a chronic course, the tympanic membrane is retracted and deformed, the lumen of the tube narrows, hearing is significantly impaired, some local areas turn red. Sclerosis of the tympanic membrane is noted. Inflammation can be complicated, which provokes the appearance of adhesions that interfere with the patency of the Eustachian tube and the bones in the ear.
How does the disease manifest in children
The anatomy of the child's ear canal differs greatly from the structure of an adult. Therefore, the child is more prone to ear diseases. The signs of Eustachitis in children are exactly the same as in adults. The following symptoms are noted:
- the presence of noise;
- nasal congestion;
- hearing loss.
What if there is inflammation in an area such as the Eustachian tube? Home treatment is not recommended. You should consult a specialist.

Diagnosis of the disease
Only a laryngologist can identify the disease. Diagnostics is based on clinical manifestations and otoscopy. Manipulation can reveal the degree of retraction of the tympanic membrane, shortening of the handle of the malleus, and a sharp protrusion towards the ear canal of a small process.
Tone audiometry is performed to determine whether hearing impairment occurs. In addition, the regent of the paranasal sinuses is carried out, the function of the auditory tubes is investigated through the Toynbee gulp test, the Poltitser test and the so-called Valsalva maneuver.
Treatment principles
How does inflammation of the Eustachian tube stop? Treatment begins after a thorough diagnosis and clarification of the cause of the inflammatory process. Having determined it, it is necessary to eliminate the pathogen so that recovery goes as quickly as possible.
The disease requires immediate treatment, since the acute form can quickly take on a chronic course and lead to persistent hearing loss. And this significantly reduces the patient's quality of life.
Drug treatment
Depends on the reason that caused it. In the case of pathology of the nasopharynx, therapy is aimed at eliminating it. In case of surges in atmospheric pressure when flying an airplane or getting up and down in the water, blowing out the ears is used with normal swallowing and a sharp exhalation with pinched nostrils and closed mouth.
Inflammation of the Eustachian tube (treatment, drugs are chosen only by the laryngologist!) medicines... The main focus is on the intake of drugs that contribute to the narrowing of the vessels of the Eustachian tube and nasopharynx. This group includes "Tizin", "Nazivin", "Rinostop", "Galazolin", "Xilen". They are dispensed without a prescription. Drops are injected into the nose 2-3 times a day. You can use these funds for no more than five days.
TO antibacterial drugs include ear drops "Polydex", "Sofradeks", "Normaks", "Dancil". Antihistamines - "Suprastin", "Erius", "Claritin", "Tavegil", "Telfast", "Zirtek" act as additional therapy.
In some cases, local hormonal agents are prescribed. For example, "Nasonex", "Avamis", "Fliksonase" are used. They have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.
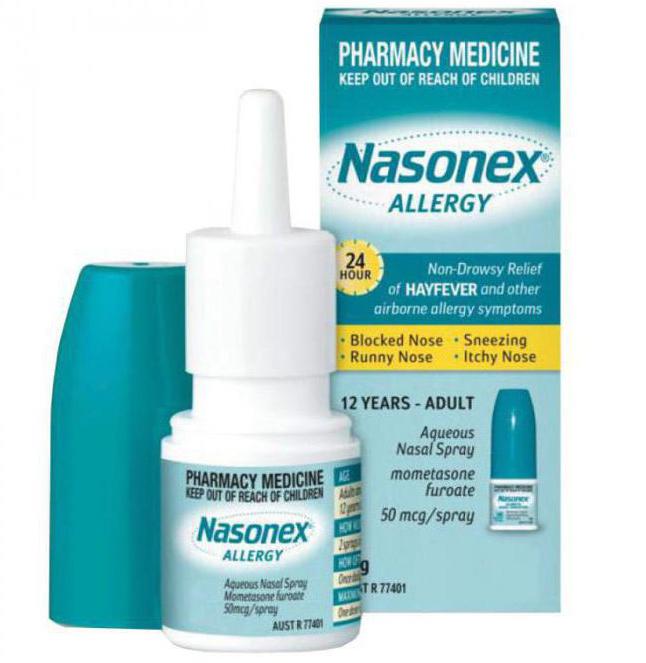
If inflammation is found in an area such as the Eustachian tube, treatment involves the use of anti-inflammatory drugs and anti-microbial agents. Usually, drugs are used that are instilled into the ear (3-4 drops three times a day). They should be applied no more than 10 days.
Furacilin and boric acid 3% are used as local preparations against inflammation. For oral administration, antibiotics such as "Amoxiclav", "Cefuroxime", "Afenoxin" can be prescribed. They are taken twice a day, at a dose of 250-700 mg, strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
Eustachian tube blowing through a catheter is highly effective. Hydrocortisone or epinephrine is administered. With correct therapy, the disease stops within a few days. If measures were taken late, then the disease can become chronic and difficult to treat.
If the process is neglected, surgical intervention may be required. An incision is made in the area of \u200b\u200bthe tympanic membrane, into which a catheter is inserted to suction fluid. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
To enhance the effect of the treatment, physiotherapy is carried out, and compresses are also used. Of the physiotherapy procedures, it should be noted UFO, UHF of the nasal region, laser therapy.
How else can you eliminate inflammation of the auditory Eustachian tube? Treatment after stopping the acute course with preserved reduced hearing involves the use of the method of blowing the auditory tubes or pneumatic massage. For blowing, the Politzer method or catheterization is used.
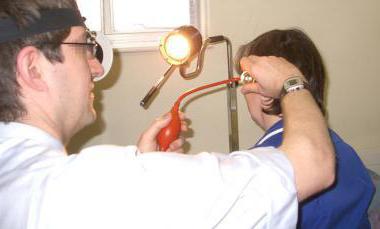
Politzer's method and catheterization
The ear is blown through the Politzer by means of a rubber balloon, which is connected to an olive by a rubber tube. An olive is inserted into the patient's nostril. The wings of the nose are pinched. To get air into the eardrum, the patient must swallow air and pronounce the word "cuckoo" loudly in syllables. When the syllable is stressed, the palatine curtain rises and is pressed against back wall pharynx. At this moment, the doctor makes a slight compression of the balloon. Air intrusion is monitored using an otoscope.
With successful manipulations, as a rule, the patient's condition is optimized after 1-3 procedures. Hearing may improve for a few days. In this case, additional blowdowns are required in 1-2 days. The procedures are carried out for 2-3 weeks.
With low efficiency of the Politzer method, the air is blown into the eardrum using a special ear catheter and a rubber balloon. After manipulation, pneumatic massage of the tympanic membrane is performed.
The essence of catheterization lies in the fact that the eardrum is supplied with variable pressure, which helps to increase its elasticity, makes it mobile, and prevents the appearance of scars leading to hearing loss.
The use of folk remedies
How else can you eliminate inflammation of the Eustachian tube? Treatment folk remedies involves the use of a number of recipes:
- Aloe juice is mixed with warm boiled water in a 1: 1 ratio. This agent is instilled into the nose every 5 hours. In addition, a tampon is moistened with it and inserted into the ear.
- Onion juice is instilled into the nose before bedtime, and a warm bulb is placed in the ear area.
- Eucalyptus, celandine lavender, yarrow are taken in equal proportions. Two tablespoons of herbal collection are poured with 0.5 liters of boiling water. The product is infused in a thermos for 12 hours. The infusion is drunk three times a day for ¼ glass.
Complications of the disease
Inflammation of the Eustachian tube (symptoms, treatment with folk remedies and medicines, we described in this article) with timely therapy, as a rule, is completely eliminated and does not cause any complications. But due to the fact that the symptoms of the disease are erased, the patient does not always get an appointment with a laryngologist on time, which provokes undesirable consequences. There may be a steady decrease in hearing, purulent otitis media in acute form, deformation of the membrane, scarring of the tissues of the middle ear. Eustachitis can also lead to complete hearing loss.
Prevention
In order to prevent inflammation of the Eustachian tube, the treatment of which is quite difficult, it is necessary to stop the diseases that provoke it in time. It is necessary to constantly strengthen the immune system, not to use a large amount of antibiotics, to give up bad habits. Be healthy!
Tubo-otitis, or eustachitis - inflammation of the auditory, or eustachian tube. At the initial occurrence, the pathology proceeds in an acute form. Lack of treatment or its untimely start lead to the fact that the disease becomes chronic. The disease is characterized by impaired ventilation in the middle ear area, which inevitably entails a rapid deterioration in hearing.
Inflammation in the area of \u200b\u200bthe auditory Eustachian tube in medicine is often considered as the initial stage of a pathology such as catarrhal otitis media. There is an inextricable link between Eustachitis and inflammation in the area of \u200b\u200bthe tympanic cavity, so doctors use two concepts that combine both of these diseases: tubo-otitis and salpingo-otitis.
Features of inflammation of the Eustachian tube
The cause of the disease, as a rule, is a pathological process that has passed from the nasopharynx to the ear area.
Mainly predecessor this disease becomes acute or chronic rhinitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis. When it first appears, the inflammation is called acute.
If it is not completely cured or not treated at all, it becomes chronic and bothers a person from time to time.
It should be noted that any form of Eustachitis is accompanied by high risk development of otitis media.
Obstruction of the tube often occurs when the nasopharyngeal opening is closed, provoked by diseases such as adenoids, choanal polyps, hypertrophy of the inferior turbinate.
The main causes of inflammation
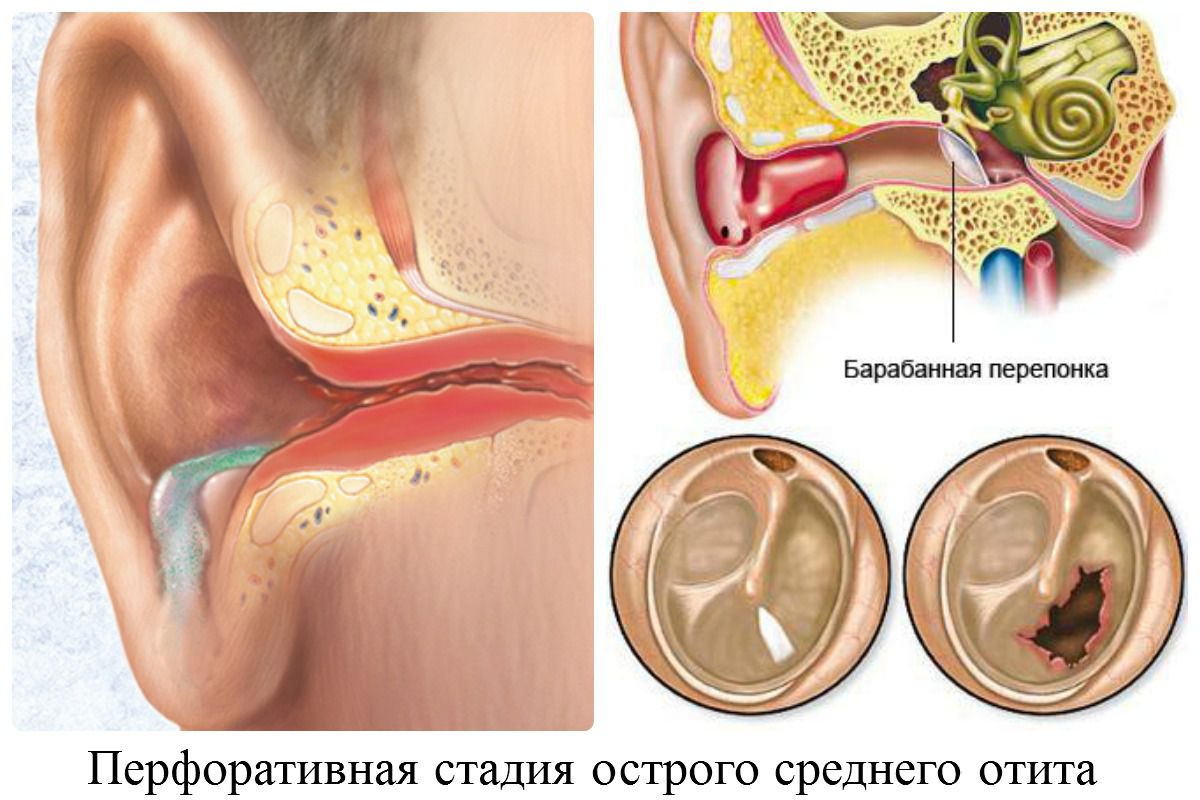
It has already been mentioned above that doctors often consider Eustachitis as the initial stage of catarrhal otitis media.
However, this disease can cause regular secondary purulent and adhesive otitis media, as a result of which hearing loss occurs.
Tubo-otitis can occur both due to the presence of chronic pathology in the body, and due to anatomical abnormalities that are quite common among the ENT organs.
The latter include, for example, rhinitis, rhinopharyngitis, polyps, adenoids, sinusitis, curvature of the septum in the nose, etc.
The provocateur of inflammation is the pathogenic microflora - staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci and similar microorganisms. It is they who provoke the pathological process in the ear.
However, such a phenomenon as an allergic reaction is not excluded. The inflammation caused by an abnormal reaction of the body in medicine is accordingly called allergic eustachitis.
Under the influence of negative factors, inflammation, infectious or allergic, occurs, which is accompanied by swelling and thickening over the entire surface of the mucous membrane. This process leads to disruption of the normal patency of the Eustachian tube and, of course, its ventilation worsens.
The eardrum sinks and then is pulled into the tympanic cavity due to a decrease in pressure in the tube - autophony occurs - ear congestion.
At the same time, the stenosis process develops in this area, the walls of the auditory tube stick together, atrophic and sclerotic metamorphoses occur in the tympanic cavity and membrane. If you don't see a specialist and start treatment, the inflammation can lead to permanent hearing loss or complete hearing loss.
Symptoms of acute inflammation of the auditory tube
This form most often develops against the background of influenza or seasonal catarrh, localized in the upper respiratory tract.
The most pronounced signs of the resulting pathology are as follows:
- Congestion of one ear or two at once;
- Resonance of your own voice - autophony, as well as noises;
- Feeling of heaviness in the head from the side of the lesion;
- A feeling of overflowing fluid in the ear, which occurs when the head is turned or tilted.
In an acute process, the patient's well-being remains stable, the temperature does not exceed the norm, there is no pain syndrome.
This form of the disease most often occurs when an infection occurs against the background of a weakened immunity in the upper respiratory tract. If treatment is absent or does not have the expected effect, the pathology acquires a chronic course that is difficult to respond to even the strongest therapy and leads to hearing impairment. Timely measures taken make it possible to get rid of the disease and its unpleasant symptoms in just a few days, to restore the patency of the pipe and hearing.
Symptoms of the chronic form of the disease
In this case, atrophic and sclerotic changes occur in the mucous membrane of the tympanic membrane and its cavity.
In the chronic course of the inflammatory process, the following symptoms are observed:

- Clouding and deformation of the tympanic membrane;
- Narrowing of the auditory tube;
- Persistent hearing impairment;
- Limited redness in certain areas;
- Retracting the membrane into the tympanic cavity.
The listed symptoms of the chronic form of the disease can only be seen by a specialist, that is, an otolaryngologist.
This pathology is accompanied by a decrease in the lumen of the auditory tube, which entails deformation of the tympanic membrane and its further retraction. Permeability is impaired, the pipe walls begin to stick together. It should be noted that the symptoms are persistent.
Inflammation of the auditory tube in childhood
Ear diseases in babies are quite common due to their peculiarities anatomical structure this zone. In children, the ear canal is shortened and straighter than in adults. For this reason, they are susceptible to various ear diseases, including tubo-otitis.
The symptomatology of pathology in babies practically does not differ from that inherent in adults:

- The presence of noise;
- Ears congestion;
- Poor audibility;
- Temporary improvement in hearing when coughing, sneezing, yawning.
Despite the fact that in children, as a rule, the disease is more severe than in adults, the temperature remains normal, there is no pain either.
These factors can complicate self-diagnosis, that is, parents will not attach importance to the symptoms that have arisen and will delay the visit to the doctor.
Treatment of acute and chronic inflammation of the auditory tube
The first thing to do is to disinfect the middle ear mucosa. Then all activities are aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process and the phenomena that followed. You also need to get rid of the adverse factors that affect the mouth of the auditory tube in case of illness.
To reduce swelling, the doctor prescribes vasoconstrictor drops for the nose. Antihistamines work in a similar way. To exclude the throwing of infected mucus, you should not blow your nose too vigorously.
Sometimes it is necessary to use blowing (catheterization) of the auditory tube. In addition, the complex of treatment necessarily includes physiotherapy procedures, for example, laser exposure, pneumomassage, UHF and UFO.
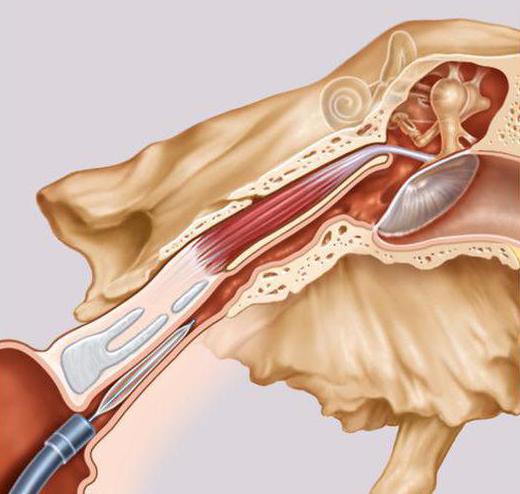
The organ of hearing is one of the most important in the human body; without it, full-fledged perception of the surrounding world is impossible. The middle ear consists of three main parts of the mastoid and tympanic cavities, as well as the Eustachian (or auditory) tube, which connects the nasopharynx to the tympanic membrane. Sometimes this pipe becomes inflamed and stops functioning fully, which can lead to serious and sometimes irreversible consequences.
Signs of inflammation of the Eustachian tube
The auditory tube is relatively small in size, on average about 3.5 cm long and about 2 mm thick, but it performs a number of very important functions: acoustic, ventilation, drainage and protective. Improper and untimely treatment of inflammation of the Eustachian tube can lead to hearing loss and even absolute deafness.
The auditory tube plays the role of not only a connecting canal, but also provides air exchange, removal of fluids from the ear cavity. It also helps maintain the optimal level of air pressure inside the organ and prevents the penetration of infection by producing mucus that destroys bacteria.
With dysfunction of this channel, its mucous membranes thicken, and the lumen narrows, as a result of which metabolic processes are disrupted and pressure inside the organ decreases, fluid stagnates and the inflammatory process begins.
The main signs of the disease:
- A feeling of congestion or water in the ear
- Tinnitus
- Deterioration in hearing quality
- The appearance of painful sensations in the ear
- Sometimes elevated temperature body, dizziness, headaches.
The initial stage of the disease, as a rule, is accompanied only by discomfort, pain and changes in body temperature are not typical for it. The danger lies in the rapid progression of inflammation: the disease can become severe in a few hours.
Specialists call the inflammation of this tube eustachitis, its simultaneous affection with the middle ear can be diagnosed as tubo otitis media, salpingo otitis media, tubotempanitis. There are two forms of the disease: acute and chronic.
In the presence of the above symptoms, it is necessary to visit an ENT doctor, only he will be able to correctly diagnose the disease and prescribe a treatment that is effective for a particular case.
Diagnosis of the disease consists in examination with an otoscope, a test for the level of hearing and determining the degree of patency of the Eustachian tube.

The infectious nature of the disease is determined by laboratory analysis of a throat swab. However, science does not stand still and more sophisticated equipment is used in progressive specialized clinics.
Eustachitis treatment
Treatment methods for Eustachitis depend on the severity of the disease and the reasons that provoked it. In this regard, it is imperative to inform the doctor about previous illnesses and a tendency to allergies. Therapeutic measures to combat this ailment have six main areas:
- Removal of swelling of the Eustachian tube. To reduce edema of the nasopharyngeal mucosa and tube, respectively, doctors prescribe the use of vasoconstrictor drops: Sanorin, Vibrocil, Tizin, Nazol, Nazivin, etc. Mucolytic agents such as Ambroskol, Sinupret and others help to eliminate the thick liquid blocking the passage.
- Relief of allergic reactions if they caused inflammation. For this purpose, the following drugs are resorted to: Claritin, Deporatadin, Suprastin, Zodak, Citrine, etc.
- Elimination of the inflammatory process. For this, a solution of penicillin in ephedrine is used, which is instilled into the nose. This procedure helps to restore the functions of the auditory tube and destroy the infectious pathogen, and has a bactericidal effect. Sometimes they resort to using local hormonal agents: Nasonex, Avamis, etc., which have pronounced anti-inflammatory properties.
- Restoring the patency of the Eustachian tube involves blowing out the ears by the Politzer method or by catheterization. They also resort to physical procedures (UHF, UFO), pneumomassage of the tympanic membrane and laser therapy in the area of \u200b\u200bthe mouth of the Eustachian tube. These measures are often used at a stage when inflammation is eliminated, but hearing is not restored.
- Strengthening the general immune system, because it is much more difficult for a weakened body to cope with inflammatory process... Vitamins and immunomodulators are excellent helpers in the fight against any infection.
- Elimination of the cause of the appearance of the disease. If necessary, the foci of chronic infection are sanitized: removal of the palatine tonsils or adenoids, therapy with antibiotics, etc.
Only a doctor is able to identify the root cause of the disease, determine the ways of recovery and the correct methods of treatment. A lot also depends on the patient: it is necessary to consult a specialist in time and follow all his recommendations.
Traditional medicine and homeopathy for inflammation of the Eustachian tube
Often, unconventional methods lead to very good results, but before using them, you should definitely consult your doctor. If an allergic reaction is the cause of Eustachitis, the use of herbal remedies can be significantly harmful. There is also individual intolerance, and side effects, only a competent doctor can take into account all the nuances and characteristics of the body.
Most popular remedies traditional medicine with inflammation of the auditory tube:
- Herbal decoctions. Apply calendula, chamomile, oak bark. These drugs are prepared quite easily: two tablespoons of the dry mixture are brewed with a glass of boiling water and infused for two hours. The mixture, in a slightly warmed form, is dripped into the nostril or ear. These plants are considered excellent antiseptics and will help reduce inflammation faster.
- Aloe and agave juices diluted with a small amount of warm boiled water are recommended to drip into the nose and use to wash the ears.
- Boiled potatoes are a well-known remedy for colds, with Eustachitis, it is also effective. Application: boil potatoes and breathe over the steam, covered with a towel for a few minutes.
- Garlic. This is an excellent remedy in the fight against infection, you need to grind it to the consistency of a gruel, add vegetable oil and leave for two weeks. The resulting infusion drip into the ears and nose.
- Wrap the onion chopped into porridge in a piece of gauze and insert into the affected ear for 10 minutes. The procedure is repeated from one to two weeks, once a day.
- Among homeopathic remedies for inflammation of the Eustachian tubes, Fitolyakka, Silicea and Damascus rose are widely used.
Folk recipes are recommended to be used in conjunction with conservative therapy; you should not rely on them entirely, neglecting the doctor's prescriptions. Yes, and it is unlikely that it will be possible to establish the initial cause of the inflammation on your own, therefore it is highly likely to drown out the disease, but not get rid of it completely.
Causes of eustachitis and preventive measures
The disease occurs due to hypothermia, against the background of a weakened immune system, due to infectious inflammation in the nasopharynx. It can manifest itself in the form of complications after influenza, sore throat, pharyngitis, acute or chronic sinusitis, etc.
It is always easier to prevent diseases than to cure them. Not complicated preventive measures help to avoid inflammation of the auditory tube:
- Timely treatment of all viral and infectious diseases
- Hardening and proper nutrition, strengthening the immune system
- Clothing for the weather and prevention of colds
- Correction of pathologies of the structure of the nasopharynx (polyps, cysts, etc.)
- Correction of allergic reactions
While watching the video, you will learn about the Eustachian tube.
Health is a precious gift. It remains to wish everyone as long as possible to own this treasure and protect it in all possible ways.

