With flu, acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections, patients often have to deal with a sore throat. Therefore, upon discovering a painful sensation in the throat, many of us first of all begin to self-medicate, using pharmacy products and drugs aimed at relieving the symptoms of the common cold and the flu virus.
In fact, sore throat is far from always associated with these diseases: in some cases, such a symptom can be disturbed under the influence of completely different factors (trauma to the throat tissue, tonsillitis, penetration of a foreign body, blood diseases, etc.).
It is impossible to determine the exact cause if you are not a professional. That is why it is so important to seek help from a specialist when pain.
How to determine the nature of a sore throat to describe to the doctor?
Despite the difficulty of making a diagnosis without the help of a doctor, the patient will be able to at least approximately determine what may be causing the characteristic sore throat. The pain syndrome manifests itself in different ways and depends on the disease that provoked it.
Pay attention to the characteristics of a sore throat. Surely, throughout your life you have already had to suffer from various colds and viral diseasesaccompanied by a sore throat, so you can compare different types of pain and identify some of their characteristics and differences.
As a rule, a sore throat can speak of a sore throat, which manifests itself when swallowing saliva and food, as well as intensifying during yawning, sneezing and some other reflexes. If you notice that the sore throat is constant and does not change (does not increase or decrease) when swallowing, then this feature may indicate that the pain syndrome is not associated with a disease of the throat itself and, most likely, is caused by other diseases.
In this case, a sore throat can be a reflex reaction to a disease of other organs and systems in the body. An example is osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Then the ENT doctor, after examining and collecting anamnesis, will refer the patient to other specialists for further examinations and clarification of the diagnosis.
Types of sore throat:
How is the diagnosis carried out? The considered types of pain sensations can often coincide in different diseases, so even if the patient thinks that he can diagnose the "ailment" on his own, he can be mistaken, since he cannot always distinguish the pain syndrome.
During the diagnosis, the otolaryngologist will pay attention to:
- external features of the throat when viewed (redness, swelling, pus, rash, ulcers, and other possible signs that may accompany pain),
- information that he will receive through the collection of anamnesis when talking to a patient.
- test results (general analyzes; a smear taken from the mucous throat; a piece of tonsil tissue, etc.)
Is self-medication acceptable? Self-medication can only be permissible for simple forms of throat disease, when the syndrome is insignificant and is characterized by a weak manifestation. However, the help of a doctor may still be necessary if no self-medication methods have yielded the desired therapeutic effect.
What diseases cause sore throat?
Consider the most common diseases that most often become the main cause of sore throat.
Dry throat syndrome
Increased drying out of the mucous throat often provokes this symptom... Usually, pain occurs when swallowing saliva or food. Dry throat syndrome can have other symptoms that are interrelated: tickling and burning.
The syndrome occurs for a number of reasons:
- after a long conversation when the voice load increases, but it is not possible to drink a sip of water to moisturize the mucous membrane;
- in the morning after sleep at the first swallowing movement (usually dry throat syndrome occurs in this case due to dry air in a room that is rarely ventilated, as well as after clotting of mucus in the throat, which accumulates during the night during sleep; the walls of the throat begin to stick together, which leads to painful sensation when they come off from each other during swallowing);
- age-related changes in the mucosa when the body lacks moisture, they can also lead to the appearance of this syndrome;
- intense thirstwhen for a long time it was not possible to drink water and moisten the throat with liquid;
- some diseases and systemic disorders in which dry throat syndrome can become one of the symptoms (for example, this phenomenon can sometimes be observed in patients with diabetes mellitus).
With dry throat syndrome, the pharyngeal mucosa gradually becomes subatrophic, thin, redness and irritation appear, and sometimes inflammatory processes develop, accompanied by slight swelling. Sore throat in most cases becomes less noticeable when the throat is wet or when saliva is swallowed repeatedly.
If dry throat occurs too often or constantly, some complications may develop one day. These include trauma to the pharyngeal mucosa and acute pharyngitis, when inflammation affects the entire throat. Most often, complications appear in autumn or winter under the influence of cold outside and dry indoor air.
Effective preventive measures to prevent acute pharyngitis and dry throat syndrome:
- wet your throat with water regularly by drinking liquid as often as possible;
- if you have a tendency to dry throat, the more you need to often moisten your throat: carry water in a bottle or thermos always with you, use aerosol sprays to irrigate and maintain freshness in the mouth use lozenges to help increase the formation of saliva in the mouth;
- before going to bed, to avoid dryness in the throat, instill in the nose olive, peanut, corn, sunflower, apricot or vegetable oil, special drops with a moisturizing effect; you can also use a 0.9% table salt solution for this;
- use at least occasionally hot food seasonings , propolis, honey, onions, hot peppers, which moisturize the mucous membrane by influencing the processes of saliva formation;
- with severe dry throat additionally take special medications from a pharmacy, after consulting a doctor before using the funds;
- so that the air in the room is not dry, hang wet terry towels 1-2 times a day on the hot battery (the moisture will evaporate and, thus, the air will be filled with it for a while); you can also purchase special humidifiers;
- ventilate the premises regularly where you are at all times to normalize the humidity level in the air.
Such methods will also help prevent or relieve sore throat by maintaining the natural moisture of the pharyngeal mucosa at all times.
Apnea syndrome (or snoring) is also called among the possible complications of increased dryness, in which a sore throat may appear. This can happen when you have difficulty breathing through the nasal cavity when you have to breathe through your mouth. If you have a tendency to snore, be sure to use the nose drops 5-10 minutes before bed. It should be noted that vasoconstrictor drugs in this case, they should be excluded, since they are not suitable for permanent use and can be harmful.
Diseases and deformities of the nose
Dryness and pain in the throat are often signs of serious pathological changes, diseases or deformities of the nose. Usually, such phenomena are observed in the southern type of aerodynamics of the nose, characterized by increased patency of the lower nasal passage.
In this case, breathing through the mouth exacerbates the situation: the syndrome of "dry throat" increases, which leads to vibration of the soft palate and tongue, snoring and discomfort. Then the doctor may prescribe medications and physiotherapy.
If a patient has been diagnosed with nasal aerodynamic disturbances, conventional drug treatments may be ineffective.
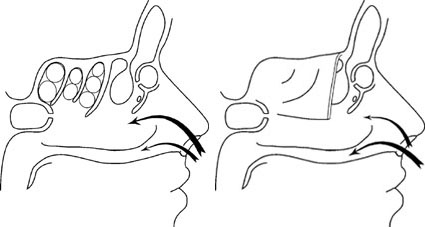
1 image - northern type of nose aerodynamics; 2 image - southern type of nose aerodynamics
Reconstruction of the southern type of nose aerodynamics to the northern type may be required. This may be necessary to protect the pharyngeal mucosa from hypothermia and dry throat syndrome. Reconstruction will eliminate Apnea syndrome.
The northern type of nasal aerodynamics is more adapted to the creation of "comfortable" conditions, which are necessary to maintain health and protect the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract.
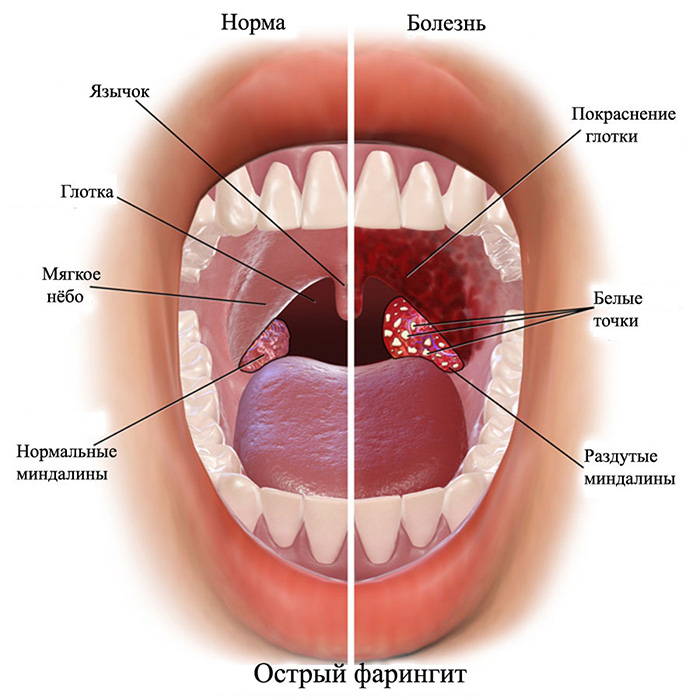
Acute pharyngitis
Acute pharyngitis is usually called inflammatory disease of the pharyngeal mucosa, which begins to develop in the absence of treatment for dry throat syndrome and a lack of moisture in the mucous membrane.
Acute pharyngitis can begin under such popular circumstances as prolonged exposure to a draft, drinking ice cream or cold drinks in the summer season (if temperatures are not correct), as well as a weakening of the functions of the immune system in the body, severe overwork.
The main symptoms of pharyngitis:
- redness of the throat mucosa;
- severe swelling of the throat;
- sharp pain in the throat when swallowing;
- increased body temperature (usually up to 38.0);
- intoxication of the body;
- pain that gets worse gradually when swallowing water.
The nature of pain in pharyngitis may vary: firstly, they can be both constant and periodic; secondly, the zone of localization of pains may differ (they can cover the entire throat or spread in different parts of it). Sometimes the pain syndrome can be so pronounced that the patient has to urgently consult an ENT doctor.
A specialist prescribes drug therapy as methods of treating pharyngitis (drugs: Ibuprofen, Aspirin, Analgin, Ortofen), and will also advise drinking more liquid (chicken broth, tea at moderately warm room temperature). Temporary home bed rest is also important to ensure adequate rest.
The minimum cycle of progression of inflammatory processes in the throat with acute form pharyngitis - two weeks, so it is advisable for the patient to be at rest at home during this entire time.
Other forms of pharyngitis and related diseases
Symptoms of acute pharyngitis are similar to signs of other forms of this disease with a different etiology. So, subatrophic, atrophic, or granular pharyngitis (granules of lymphoid tissue appear), lateral pharyngitis (vertical rolls of lymphoid tissue form on the lateral sides of the pharynx) can also be accompanied by severe sore throat.
Chronic pharyngitis is especially difficult to tolerate in people suffering from nicotine addiction. Being a neuroparalytic poison, nicotine adversely affects the mucous membrane of the pharynx, significantly reducing its natural protective functions.
When symptoms of pharyngitis appear, the smoker needs to give up cigarettes for a long time in order to speed up recovery and avoid the risk of possible complications.
Influenza, colds and sore throats. Acute pharyngitis sometimes develops against the background of other diseases. Statistics show that quite often the cause of acute pharyngitis is flu or colds, accompanied by a high fever. In such a situation, sore throat can usually appear with swallowing movement.
When a patient has a sore throat, the palatine tonsils become very inflamed, sore throat and severe dryness occur. In this case, sore throat is localized on the side, affecting one or two sides of the tonsils at the same time.
With angina, pain in the throat is usually pronounced, so the patient may have problems when swallowing and eating, and decreased appetite. Angina is dangerous because it is fraught with serious complications and the development of other diseases, decreased immunity, diseases of the liver, heart and kidneys. Therefore, it is so important to immediately consult an otolaryngologist.
Sore throat symptoms:
- enlargement of the tonsils (tonsils);
- formation of purulent plaque on the glands in the form of a rash or large focal inflammation;
- increase in jugular and regional lymph nodes accompanied by severe soreness;
- spilled foci of purulent deposits (most often with Vincent's angina);
Depending on the type of inflammation and swelling of the palatine tonsils, the localization of foci of inflammation, several types of angina are distinguished (see diagram).
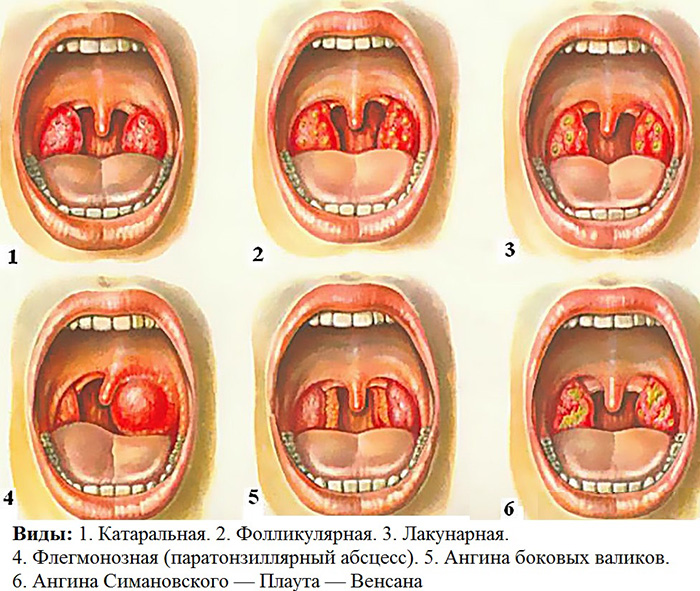
Angina is dangerous with complications such as choking when the airways are blocked, which can occur with improper treatment or untreated. With pharyngeal sore throat, sore throat is localized below or in the middle.
Often, angina manifests itself in other diseases. For example, with agranulocytosis, mononucleosis, diphtheria, scarlet fever, infectious diseases. The patient may need the help of different specialists (first of all, an otolaryngologist and therapist). It is necessary to follow all the doctor's recommendations and complete the full course of treatment, as sore throat and sore throat may recur after inadequate treatment and be accompanied by severe complications (for example, an abscess, in which an aggressive abscess forms in the patient's throat).
Paratonsillar abscess
Forming in the submucous area of \u200b\u200bthe pharynx, paratonsillar abscess usually becomes a severe complication of angina. This abscess causes progressive sore throat that can affect one or both sides of the throat at once. Sometimes the patient may feel that the pain is localized throughout the throat.
When the pain intensifies, there is a feeling of fullness, pronounced swelling, swelling of the mucous membrane, while the lumen of the pharynx may partially or completely overlap, which subsequently makes breathing difficult. It is difficult for the patient in such a situation to open his mouth, since with trismus of the masticatory muscles he often experiences severe pain due to enlarged jugular lymph nodes in the neck.
This disease is also dangerous because the soft tissues that surround the enlarged abscess cannot contain it: it destroys them and penetrates through the fistula to the outside. This process tends to make the sore throat a little weaker, and the swelling also becomes less pronounced. Therefore, sometimes it may seem to the patient that he has begun to recover.
This is actually a false impression. When a spontaneous opening of the abscess occurs, a certain amount of purulent discharge comes out, but at the same time there are still many remnants of pus in the cavity, which will "support" the inflammatory processes for a long time.
Sometimes, with a pharyngeal abscess, pus enters the surrounding soft tissues, which also poses a serious threat to the patient's health: pus begins to spread throughout the pharyngeal mucosa, reaching the space between the heart and lungs. With such a complication, there will be a need for urgent hospitalization of the patient and further surgical intervention.
Penetration of a foreign body into the throat
A foreign body can enter the pharynx and "get stuck" on the tonsils or mucous membrane of the throat during exhalation / inhalation, as well as during meals. A foreign body is the debris of food, various materials and tissues that accidentally penetrate the oral cavity and remain in the pharynx. Microparticles can harm the soft tissues of the throat, seriously damage its mucous membrane.
The nature of the pain symptom in the throat when a foreign body enters the pharynx is usually characterized by a stabbing or cutting attack of pain. It can occur with swallowing movement.
An attempt to independently remove a foreign body can lead to trauma to soft tissues and a worsening of the situation. Therefore, it is important to call a doctor, since without his help it will be not only difficult to cope with the problem, but also life-threatening.
Most often, a fragment of meat or fish bone becomes a foreign body, which breaks off when swallowing and chewing food, getting stuck in the pharyngeal wall. If you dare to push through foreign bodyto swallow, you can severely injure the wall of the pharynx. A complication can be an abscess, accompanied not only by severe sore throat, but also bleeding, swelling and difficulty breathing.
Discomfort in the throat is an alarming symptom that signals the presence of pathological processes in the airways. The pharynx is part of the respiratory and digestive tube, which on one side connects the oral and nasal cavity, and on the other - the larynx with the digestive tract.
Due to the anatomical features of the structure, the causes of sore throat when swallowing may lie in the dysfunction of not only the ENT organs, but also the thyroid gland or gastrointestinal tract.
Untimely treatment of septic and aseptic inflammations leads to edema of the mucous membranes and narrowing of the lumen in the airways.
A critical decrease in the inner diameter of the pharynx makes breathing difficult and causes hypoxia. If pain, perspiration and a feeling of squeezing of the pharynx are found, it is necessary to undergo an examination and appropriate treatment.
Etiology
If to the patient, the causes of discomfort may lie in the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes. Infection of the upper airways is one of the key causes of the appearance of an unpleasant symptom. However, in some cases, painful sensations in the pharynx are caused by mechanical injury to the ciliated epithelium, proliferation of lymphadenoid tissues, cardiovascular disorders and malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract.
Therapy of pathologies of any etiology should begin with determining the causes of its occurrence. Illiterate treatment of the disease can lead to a deterioration in well-being and the development of severe complications. Why does my throat hurt when swallowing? The main reasons for the appearance of discomfort in the throat include:

In some cases, perspiration and pain in the throat when swallowing saliva result from inappropriate intake of antibacterial and hormonal drugs.
For this reason, local immunity decreases in the mucous membranes of the ENT organs, which stimulates the reproduction of conditionally pathogenic fungi such as Candida. The presence of an unpleasant symptom for two or more weeks can be a manifestation of more serious diseases, such as malignant tumors, AIDS, etc.
Physiology of pain
Why is it painful to swallow? Pain is an unpleasant sensory experience that results from tissue damage. In the mucous membrane of the ENT organs there are many nociceptors, when excited, discomfort appears. Specific receptors can be excited when exposed to mechanical, chemical, and thermal stimuli.
Aching, non-intense pains most often indicate the presence of chronic inflammation.
The activation of pain receptors in the peripheral nervous system signals the body about the presence of harmful processes in the tissues. Septic inflammation, burns and tissue proliferation of the ciliated epithelium excite nociceptors, which, through nerve cells, transmit impulses to the corresponding parts of the brain. Painful sensations signal the danger of disease and tissue damage by pathogens or cancer cells.
Infectious diseases
If it is painful to swallow saliva, the causes of discomfort may be associated with septic inflammation of the ENT organs. Infectious diseases most often provoke painful sensations in the pharynx. Bacterial, fungal and viral infectious agents provoke pathological changes in tissues. Metabolites of pathogens accumulate in the ciliated epithelium, which leads to intoxication and the appearance of catarrhal or purulent inflammation.
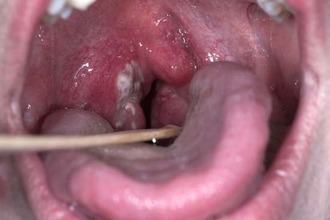 In most cases, unpleasant sensations when swallowing occur in the case of the development of the following pathologies:
In most cases, unpleasant sensations when swallowing occur in the case of the development of the following pathologies:
- pharyngitis - septic inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa associated with the multiplication of pathogens of a bacterial and viral nature;
- angina - inflammatory processes in the tissues of the lymphadenoid ring and palatine tonsils, accompanied by pain in the pharynx when swallowing saliva;
- paratonsillitis is a common complication after angina, characterized by damage to the tissues surrounding the tonsils;
- laryngitis - catarrhal inflammation of the larynx due to the development colds (measles, tonsillitis, scarlet fever);
- mononucleosis - acute inflammation tissues of the oropharynx, accompanied by damage to the lymph nodes;
- scarlet fever - infectious lesion ENT organs with streptococcal flora, characterized by symptoms of intoxication, pain in the pharynx and fever;
- swine flu is a severe viral pathology, the manifestation of which is pain in the throat, pyrexia, rhinitis, vomiting, diarrhea, etc.
Delayed treatment infectious diseases can cause serious complications. Generalization of pathological processes leads to damage to vital organs and systems, which is even fraught with death.
A clear sign of septic inflammation of the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract is subfebrile and febrile fever.
Throat injury
Injury to the mucous membranes of the airways - common reason the appearance of discomfort when swallowing saliva. The pharynx can hurt as a result of tissue damage from solid food, chemicals, toxic fumes, hot steam, etc. Due to the nature of the damage, injuries are divided into several categories:

Cicatricial formations lead to a narrowing of the lumen of the airways, which is fraught with difficulty breathing.
Oncological diseases
Why is the throat so bad and it hurts to swallow? Increased pain when swallowing, coupled with a feeling of squeezing the pharynx, may be associated with the appearance of benign and malignant tumors. In case of the appearance of neoplasms in the ENT organs, patients often complain of dry cough, perspiration, hoarseness, etc.
Due to the anatomical features of the structure of lymphadenoid tissues, tumors are most often formed in the palatine tonsils. Much less often, neoplasms occur on back wall pharynx and soft palate. Malignant tumors progress rapidly, therefore, if characteristic symptoms appear, you should seek help from a specialist.
On early stages development of lymphosarcoma, epithelinomas and reticulosarcomas are easily amenable to surgical and drug treatment. However, it should be borne in mind that untimely elimination of cancers can lead to metastasis and the occurrence of pathological changes in the thyroid gland. In addition, as tumors develop, it becomes difficult to breathe, which can lead to suffocation.
Venereal diseases
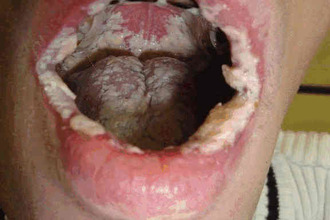 Painful sensations when swallowing, perspiration and inflammation of the mucous membranes of the ENT organs can be a symptom of the development of a genital infection. Hoarseness of the voice, swelling of the throat and an increase in regional lymph nodes may be associated with the development of pathologies such as:
Painful sensations when swallowing, perspiration and inflammation of the mucous membranes of the ENT organs can be a symptom of the development of a genital infection. Hoarseness of the voice, swelling of the throat and an increase in regional lymph nodes may be associated with the development of pathologies such as:
- syphilis - venereal bacterial disease, the causative agent of which is treponema; the introduction of pathogens into the ciliated epithelium leads to tissue compaction and chancre formation; as a result of a decrease in local immunity, microbial flora penetrates into the affected area, which causes purulent processes;
- gonorrhea - a venereal pathology that occurs as a result of lesions of the genitals with gram-negative diplococcus; untimely treatment of the disease leads to damage to the mucous membranes of the oropharynx, conjunctiva and intestines.
Extragenital chancres on the mucous membranes of the throat can provoke the development of meningoneuritis, which is fraught with atrophy of the optic and auditory nerves.
Some clinical manifestations sexually transmitted diseases are difficult to distinguish from tonsillitis symptoms. Syphilitic inflammation of the oropharynx is fraught with the development of severe systemic and local complications. For this reason, if a purulent plaque is found on the palatine tonsils and mucous membrane of the oropharynx, it is undesirable to postpone a visit to a specialist for a long time.
Vegeto-vascular dystonia - pathological changes in the autonomic nervous system, characterized by a decrease in the elasticity of blood vessels in internal organs and systems. It is often complicated by hyperventilation syndrome - a disturbance in the respiratory regulation system.
Intensification of breathing leads to drying out of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx, as a result of which there are uncomfortable sensations.
 Vegeto-vascular dystonia can be complicated ischemic disease hearts, bronchial asthma and hypertension.
Vegeto-vascular dystonia can be complicated ischemic disease hearts, bronchial asthma and hypertension.
Pathological changes in the vessels impede normal gas exchange in the tissues, as a result of which their nutrition worsens and reactivity decreases.
Due to a decrease in general and local immunity, the risk of developing infectious pathologies increases. Septic inflammation of the airways inevitably leads to painful sensations when swallowing saliva.
Gastroesophageal reflux
Violation of gastroesophageal reflux can lead to the release of gastric juice into the upper airways... A decrease in the tone of the muscles responsible for the work of the lower esophageal sphincter often causes aspiration of gastric masses. Corrosive juices irritate the mucous membrane of the pharynx and provoke the appearance of microcracks and even burns.
The gradual drying out of the ciliated epithelium is accompanied by tissue degeneration and the formation of ulcers on the inner surface of the airways. The problem is compounded by the fact that gastric juice is aspirated several times a day, which is one of the causes of chronic sore throat. A decrease in local immunity creates conditions for the development of opportunistic organisms that cause septic inflammation and the formation of abscesses in the ciliated epithelium.
Cervical osteochondrosis is one of the causes of the "pharyngeal migraine". Dystrophic changes in the joints, accompanied by damage to the intervertebral discs, lead to the development of an orthopedic disease. In the case of the development of pathology, patients complain of pain and a feeling of a coma in the throat, perspiration and shortness of breath.
Mineralization of the cartilage tissue immobilizes the vertebrae and creates an excessive load on the nerve roots.
 Squeezing nerve endings causes sore throat, radiating to the ear, back of the head, collarbone, heart and tongue.
Squeezing nerve endings causes sore throat, radiating to the ear, back of the head, collarbone, heart and tongue.
The problem can be solved in the case of a timely visit to a neurologist. It should be understood that the treatment of osteochondrosis is to prevent the progress of degenerative changes in the spine and to eliminate pain due to damage to the spinal roots.
In case of ineffectiveness of drug therapy, the patient is prescribed physiotherapy, manual therapy, spinal traction, massage or surgical treatment.
Neurotic disorders
A functional impairment of swallowing may be associated with spasm of the pharyngeal muscles. A hysterical lump (neurotic dysphagia), in which the swallowing reflex is impaired, often occurs as a result of psychoemotional overexertion, panic attacks or depression.
Excessive stress on the nervous system associated with a severe mental state leads to impaired conduction of nerve impulses. Thus, an involuntary contraction of the pharyngeal muscles occurs, as a result of which pain and discomfort appear. Patients may complain of a lump in the throat, which makes it difficult to swallow saliva and breathe normally.
In the absence of treatment, patients concentrate on their feelings, which leads to the development of cancerophobia. If a problem arises, you need to seek help from a psychotherapist. Therapy with antidepressants and neuroleptics allows you to eliminate the feeling of anxiety, depressive conditions and, accordingly, the psychosomatic causes of the development of pathology.
If the soreness of the pharynx is accompanied by rapid fatigue, muscle myalgia and apathy, this may indicate the development of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS).
 The disease occurs as a result of neurosis of individual centers in the autonomic nervous system. The provocateurs of pathological changes are:
The disease occurs as a result of neurosis of individual centers in the autonomic nervous system. The provocateurs of pathological changes are:
- constant stress;
- excessive intellectual workload;
- hypodynamia;
- unfavorable ecological situation;
- viral infections;
- chronic diseases.
If the disease develops, patients feel discomfort when swallowing saliva, constant headaches, joint and muscle fatigue, cognitive impairment, etc.
Until now, the key reasons for the development of CFS remain unknown. The most convincing theory is the viral origin of the pathology, according to which the triggers of chronic fatigue are retroviruses, herpesoviruses, enroviruses, cytomeloviruses, etc.
The development of CFS may indicate the presence of immunological disorders, as evidenced by an increase in the concentration of immunocompetent cells in the blood.
Chronic fatigue syndrome often becomes a complication of somatized disorders and depressive conditions. For the treatment of pathology, antidepressants, mineral complexes, autogenic training, psychotherapy and unloading and dietary therapy are used. It should be understood that the earlier treatment is started, the higher the chances of eliminating diseases and discomfort in the throat will be. A visit to a specialist cannot be postponed if, in addition to pain in the pharynx, there is hyperthermia, heartburn, fever, hoarseness, weight loss, severe abdominal pain, etc.
A sore throat is a symptom of many diseases. Painful sensations may occur if inflammatory process, various neoplasms and injuries. Often, a sore throat when swallowing appears with angina (see), when the tonsils are inflamed, and during.
In addition to pain, these diseases are characterized by fever, redness of the mucous membrane of the pharynx and palate, enlargement of the tonsils, as well as a purulent plaque on them. But there are many other factors that can trigger pain in the larynx and throat.
Neoplasms
Benign neoplasms, particularly large adenomas, may cause mild pain when swallowing. The formation of malignant tumors is invariably accompanied by regular or recurrent pain. Most often they are located on the soft palate or palatine tonsil, but can also appear on the back of the pharynx.
The nature and strength of pain depends on the localization of the neoplasm and its type:
- With lymphoma, you may have difficulty swallowing, a feeling of a lump in your throat.
- Epitheliomas (tumors from the epithelium) begin to form on the surface, gradually turning into regional lymphadenitis with a wooden density of nodes. The lesion increases as the neoplasm penetrates deep into the tissues, and the pain can spread not only to the throat and pharynx, but also to the ears.
- Lymphosarcoma causes pain and makes breathing and swallowing difficult.
- Reticulosarcoma is similar in symptoms to lymphosarcoma, but much earlier it begins to spread metastases.
- External tumors that can cause sore throat include thyroid cancer. A person has difficulty swallowing, the neck begins to hurt and there is a feeling that an object is stuck in the throat. As it grows, the growth makes breathing difficult, leading to neck swelling, shortness of breath, coughing and hoarseness.
Sexual infections
Some sexually transmitted diseases can cause a sore throat. These include the following diseases:
Pharyngeal gonorrhea
At the initial stage, it manifests itself as a common angina. The patient's throat begins to ache, and upon examination, the doctor discovers an abundant purulent plaque on the tonsils. You can get the disease through oral sex. Also, the disease can develop in newborns when a pathogenic microorganism enters the child's body from the mother during childbirth.
Syphilis of the pharynx
The first symptoms of the disease appear about a month after infection. At the site of penetration of the causative agent of the disease (pale treponema) into the mucous membrane, a hard chancre appears - an ulcer with a smooth bottom and dense edges. Cervical and submandibular lymph nodes begin to enlarge, they become hard and painful. The chancre does not hurt until the onset of secondary suppuration, which occurs after the penetration of microbes into the ulcer. After the development of secondary syphilis in 2-3 months, the pharynx is covered with numerous bright bumps (syphilis). The patient begins to complain of a dry cough, and when the pathological process spreads to the larynx, the voice becomes hoarse.
See also: ""
Sore throat without fever
Sore throat without high temperature, causes not only discomfort when talking and eating, but also alarms the patient. A similar symptom is characteristic of a large number of different diseases and other types of damage to the pharynx:
Chronic pharyngitis
Has no pronounced symptoms (intoxication and elevated temperature). Depending on the type of pharyngitis (catarrhal, granular or atrophic), the symptoms also differ:
- Atrophic pharyngitis expressed with difficulty swallowing food and dry throat. Quite often, the disease is accompanied by bad breath and bleeding of small vessels in the pharynx. Patients are forced to drink plenty of fluids to relieve dry mouth and throat. Atrophic pharyngitis often develops against the background of digestive diseases and subsides after the treatment of gastritis, ulcers or duodenitis is completed. The terminal stage of the disease is accompanied by thinning of the mucous membrane of the pharynx, the formation of crusts, erosions and (ozenes).
- Catarrhal pharyngitis or with hypertrophy of the mucous membrane, the patient has a sore throat. Sometimes there may be a scratching or tickling sensation in the throat. Some patients complain of a foreign body sensation in the throat, which, however, does not interfere with swallowing food. To get rid of this sensation, the patient is forced to swallow saliva frequently.
- Granular pharyngitis manifests itself with the same symptoms as catarrhal, but they are more pronounced. The causes of granular pharyngitis can be acute pharyngitis, gastroesophageal reflux (in which the contents of the stomach are thrown into the esophagus). Alcohol abuse, smoking, allergies and dusty air can be factors contributing to the development of pharyngitis granulosa.
Acute pharyngitis (allergic, nutritional, or toxic)
Causes severe pain and difficulty in swallowing. The pharynx is irritated by various substances that provoke pain. Similar symptoms can appear after smoking a cigarette. The main symptoms are redness and irritation of the pharynx, edema appears on it, and the mucous membrane becomes dry and filled with blood. In some patients, strep throat is accompanied by sore throat and dry throat, coughing, or sharp bouts of pain in the form of tingling.
Retropharyngeal abscess
It occurs when the mucous membrane of the pharynx is damaged by a foreign body. If the damage is deep, an abscess forms in its place, which causes a sore throat. They occur due to infection in the affected area. Puncture wounds or sharp foreign bodies trapped in the throat can cause similar complications. Symptoms begin to appear already two to three days after the injury:
- Painful sensations appear while eating
- It becomes difficult to swallow saliva
- Difficulty breathing
- Intoxication develops, which is later accompanied by an increase in temperature to 40 degrees
- Regional lymphadenitis occurs
- The patient is forced to keep his head in an unnatural position.
An abscess can be detected with a thorough examination of the pharynx, and an X-ray examination will help confirm the diagnosis.
Mucosal injury
They often cause sore throat. The mucous membrane can be damaged mechanically (foreign bodies, cuts, gunshot wounds), chemical (vinegar, acid, alcohol) and thermal (burns).
Mechanical damage to the pharynx
Most often it occurs due to foreign bodies trapped in the pharynx. A sharp object can get stuck in the back of the oropharynx. Very often, children get such injuries, who can swallow small parts of toys, various balls or seeds from fruits.
Very often, mechanical damage to the pharynx can cause bone from fish or meat, glass from broken dishes, and children sometimes try to bite through Christmas toys or ampoules with medicines. Only those foreign bodies that are stuck in the upper part of the pharynx can be quickly noticed and easily removed. If the item is stuck in the middle and lower section, it will be difficult to notice. It can stay in the throat for a long time, causing inflammation. And if a large object is hit, the patient may even have difficulty breathing. An ENT can detect a foreign body or a site of inflammation during retropharyngoscopy.
Thermal burns
Often they occur in everyday life due to the negligence of the person himself if he drinks too hot liquids. The burn occurs mainly in the mouth, but hot tea, coffee, or soup can go down the throat and cause a burn.
With the first degree of burns, damage to the epithelium occurs, which sloughs off 3-4 days after damage. In this case, the pharynx becomes red and edematous, and the patient may feel pain in the esophagus and a burning sensation in the throat when swallowing.
The second degree is expressed not only in the formation of a scab on the mucous membrane, but also common symptoms intoxication, in particular - an increase in temperature. After about a week, the scab disappears, and bleeding wounds form in its place. All these defects are covered with scars during healing.
The third degree of a burn is characterized by extensive lesions of the mucous membrane under the formed scabs. They fall off two weeks after injury, and erosions and ulcers form in their place, which heal very slowly and leave scars. Such scars on the pharyngeal mucosa can narrow it, and the patient's temperature rises and burns with multiple organ failure can begin. As complications of the third degree of thermal burns, tracheobronchitis, laryngitis, perforation, bleeding and inflammation of the mucosa occur.
Chemical burns
The most severe type of damage to the pharynx, which is difficult to treat. The speed of treatment depends on how long the throat has been exposed to the chemical toxin. The longer this process lasted, and the more concentrated the solution was, the deeper the mucous membrane is affected. With chemical burns, extensive erosions and bleeding with infection can occur. Patients complain of cutting sore throat. A scab appears in the mouth, by the color of which you can determine which solution caused the burn. When exposed to vinegar and alkali, the scab will be white, under the influence of sulfuric and hydrochloric acid, a brown coating is formed, and nitric acid gives a yellow scab.
These burns lead to rough scars that constrict the throat. The patient may be forced to feed through a special tube or drip. The patient will have to undergo surgery and a long rehabilitation course of treatment. Acetic acid poisoning, in addition to damage to the pharynx, leads to renal failure, in which the patient needs hemodialysis.
Sore throat with fever
Sore throat is one of the characteristic symptoms of acute pharyngitis. In addition to pain, patients feel a sore throat and dryness, and in some, the process of the disease is accompanied by the formation of viscous mucus. With an allergic nature of the disease, it is transparent, and with a bacterial nature, it is yellow or green.
With pharyngitis, the patient's temperature rises to 37.5 degrees, and intoxication appears (headache, muscles and joints). Lymph nodes in the neck and under the jaw may enlarge. Examination shows swelling and redness of the mucous membrane of the throat (most often on the tonsils, palate and palatine arches). Pharyngitis differs from angina in that with this disease, a purulent plaque does not form in the pharynx and on the tonsils (see).
Acute infectious pharyngitis, which is accompanied by a sore throat and fever, is divided into several types:
- Fungal (candidal)
- Viral - caused by adenovirus, parainfluenza, rhinovirus, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus and coronaviruses.
- Bacterial develops when streptococcus, staphylococcus, haemophilus influenzae and mycoplasma enter the body.
- Allergic (toxic) occurs when the mucous membrane is irritated by smoke, cigarette tar, chemicals and low temperatures.
- Radiation pharyngitis develops under the influence of ionizing radiation (for example, with radiation therapy).
- Pharyngomycosis is a fungal infection of the pharynx with Candida albicans. The disease often appears after treatment with glucocorticosteroids, antibiotics, against the background of immunodeficiency or diabetes mellitus. This type of disease has significant differences from the types described above. The patient has more pronounced discomfort in the throat (constant burning, scratching and dryness). Severe symptoms of intoxication appear. Sore throat may be mild, but it worsens when saliva is swallowed and while eating, and may radiate to the jaw, ear and neck. A distinctive feature of pharyngomycosis is a white or yellow coating on the tonsils, palatine arches and soft palate. After the plaque is rejected or removed, foci of bleeding appear at the site of the lesion, which only intensify the pain and can cause the development of a secondary infection.
It is possible to distinguish pharyngomycosis from diphtheria, in which plaque also appears in the throat, by sowing from the throat and nose for the presence of Lefler's stick.
The development of bacterial or viral pharyngitis is possible only under concomitant conditions under which pathogens begin to actively multiply. These include hypothermia, starvation, taking drugs that suppress immunity, as well as chronic diseases in a neglected form.
Other diseases that cause sore throat
There are a number of other diseases that are not related to the respiratory system or oral cavitywhich can cause sore throat. These include:
Neurotic disorders
Anxiety attacks and somatized depression can cause difficulty swallowing and sore throat. Patients complain of a feeling of a lump in the throat, which makes it difficult to swallow and breathe. A general severe nervous condition only aggravates the situation, patients begin to focus on their painful sensations and they develop carcinophobia. To get rid of this condition, you need to contact a psychotherapist, undergo a rehabilitation course and drug treatment antidepressants.
Causes a condition that doctors call "pharyngeal migraine." It causes a feeling of a lump in the throat, which may be accompanied by pain and difficulty swallowing. Pressure on the third root causes pain behind the ear, sensation of enlargement of the tongue. If the fourth root is affected, pain in the heart and collarbone joins. A qualified neurologist can solve the problem.
Laryngeal pain
Sometimes pain can occur not only in the throat, but also in the larynx with each swallowing. The following factors can cause this pathology:
Since diseases, the symptom of which is a sore throat or pharynx, are quite serious, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor at the very first signs of the disease.
